Hack The Box - Meow

Howdy my fellow Cyber Enthusiasts! Welcome to the first Starting Point Hack The Box offers. I am excited to embark on this journey with you. So, without further ado, let’s dive in! :)
Need to embark on an exciting journey on Hack The Box? Sign up now using the following Link.
Remember to change the IP adress to your allocated one! :)
There are 2 options available to connect to our machine. First using Pwnbox or secondly using OpenVPN.
I need to mention that if you are using the first option (Pwnbox) you can follow this guide, regardless if you are using Windows, Mac OS or Linux. This is the case, because a new tab will open in your web browser and there you can interact with the target machine.
Now, if you are using Ubuntu-based distros, you can following this guide using the second option as well, but it will not work with a Windows OS for example.
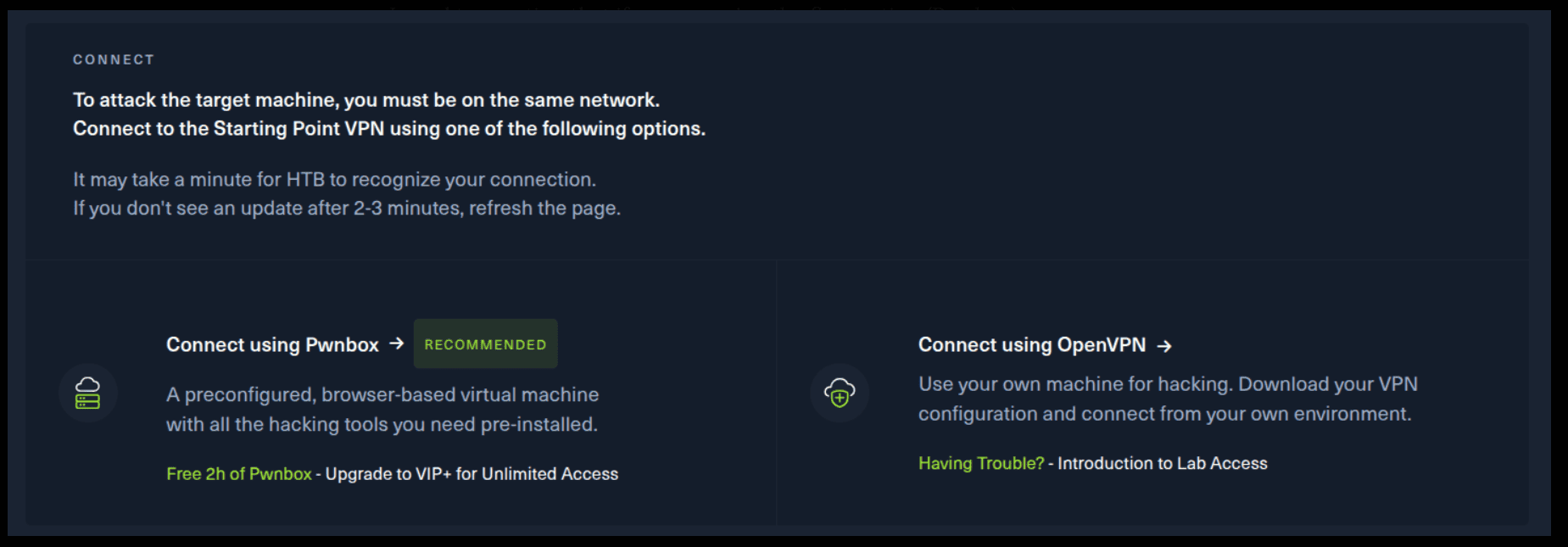
If you want to use the first option, it is very simple. Just click on the option and follow the instructions (Start Pwnbox). A new tab will open up and there you can interact with the machine.
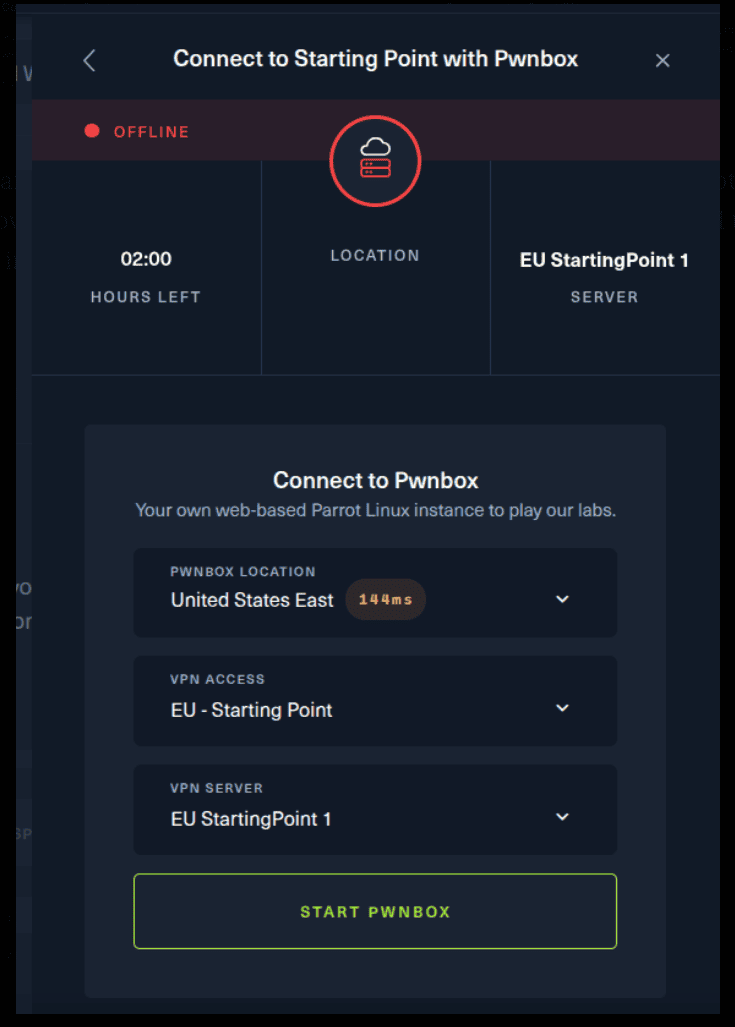
For the second option, things are a bit more complicated. You click on the “Connect using OpenVPN” and the follow section appears. Click on “Download VPN” and save the file on your desired folder.
Then open up the terminal and navigate to the folder that you’ve downloaded the .ovpn file. Then, type the following command (change the filename accordingly).
sudo openvpn root.ovpn
To make sure you are connected to the Hack The Box network type the following command in the terminal.
ip a s
You should see a new connection under the tun0 section. For example, I got a inet 10.10.15.55/23.
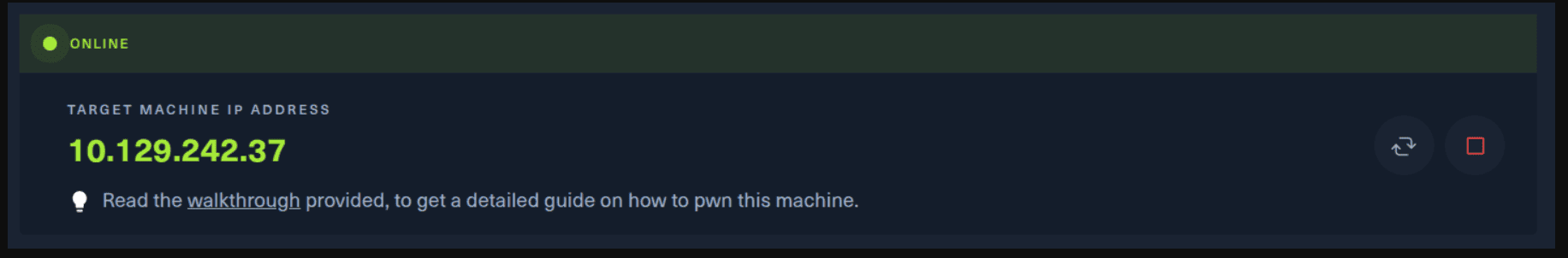
Next, you click on the “Spawn the target machine and the IP will show here“. Wait for a couple of seconds and a target machine IP address will appear. To make sure you can interact with the machine, you can ping it using the terminal to make sure it responds back.
ping -c 3 10.129.242.37
PING 10.129.242.37 (10.129.242.37) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.129.242.37: icmp_seq=1 ttl=63 time=59.3 ms
64 bytes from 10.129.242.37: icmp_seq=2 ttl=63 time=58.0 ms
64 bytes from 10.129.242.37: icmp_seq=3 ttl=63 time=58.0 ms
--- 10.129.242.37 ping statistics ---
3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2002ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 57.965/58.439/59.335/0.633 ms
So, let’s proceed with the questions.
Task 1
What does the acronym VM stand for?
Virtual Machine
In computing, a virtual machine (VM) is the virtualization or emulation of a computer system. Virtual machines are based on computer architectures and provide the functionality of a physical computer.
Task 2
What tool do we use to interact with the operating system in order to issue commands via the command line, such as the one to start our VPN connection? It's also known as a console or shell.
terminal
You probably knew this one. It is that program we are using to issue and execute our commands, such at the ping command covered above.
Task 3
What service do we use to form our VPN connection into HTB labs?
openvpn
Remember the following command? openvpn is the service we are using to form the connection with the HTB labs.
sudo openvpn root.ovpn
Task 4
What tool do we use to test our connection to the target with an ICMP echo request?
ping
Same one again! Here is a little refresher.
ping -c 3 10.129.242.37
PING 10.129.242.37 (10.129.242.37) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.129.242.37: icmp_seq=1 ttl=63 time=59.3 ms
64 bytes from 10.129.242.37: icmp_seq=2 ttl=63 time=58.0 ms
64 bytes from 10.129.242.37: icmp_seq=3 ttl=63 time=58.0 ms
--- 10.129.242.37 ping statistics ---
3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2002ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 57.965/58.439/59.335/0.633 ms
Task 5
What is the name of the most common tool for finding open ports on a target?
nmap
You probably don’t know this one. Here is a little trick to know more about a tool if you are using Linux. You can issue the following command in your Linux terminal to learn more about nmap.
man nmap
If you want to learn more information about a tool used in a Linux distribution you can use man in front of your desired tool. For instance, if you wanted to learn more about ping, you will use the following command.
man ping
In case you are wondering, Nmap (Network Mapper) is a network scanner created by Gordon Lyon. Nmap is used to discover hosts and services on a computer network by sending packets and analyzing the responses. Nmap provides a number of features for probing computer networks, including host discovery and service and operating system detection.
Task 6
What service do we identify on port 23/tcp during our scans?
telnet
sudo nmap -sV 10.129.242.37
Stats: 0:02:41 elapsed; 0 hosts completed (1 up), 1 undergoing Service Scan
Service scan Timing: About 0.00% done
Nmap scan report for 10.129.242.37
Host is up (0.060s latency).
Not shown: 999 closed ports
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
23/tcp open telnet?
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 167.48 seconds
Here is another trick! Go the terminal and type the following command.
man nmap
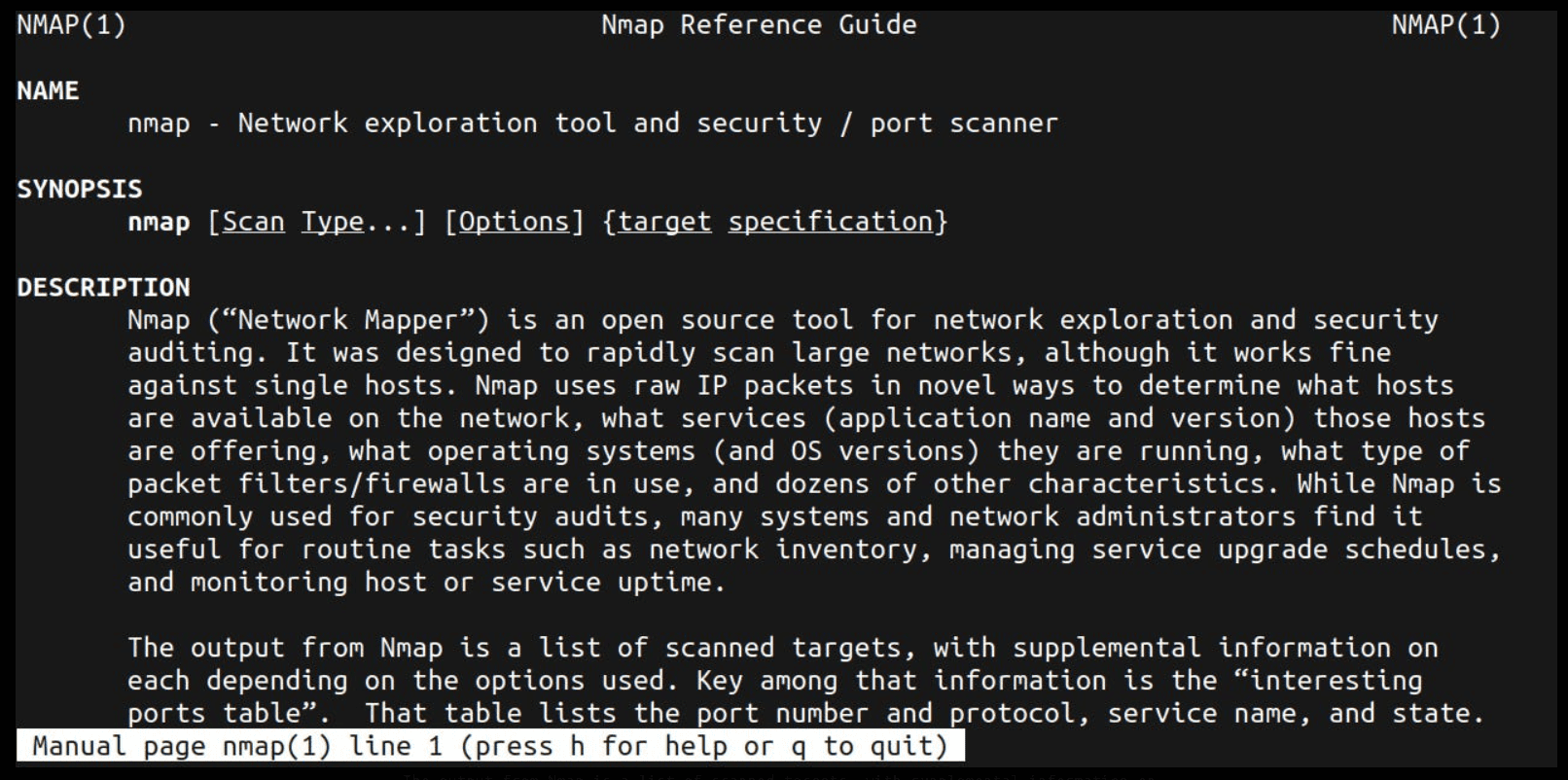
Now, type /sV and press Enter. It will update at the left bottom side of the terminal.
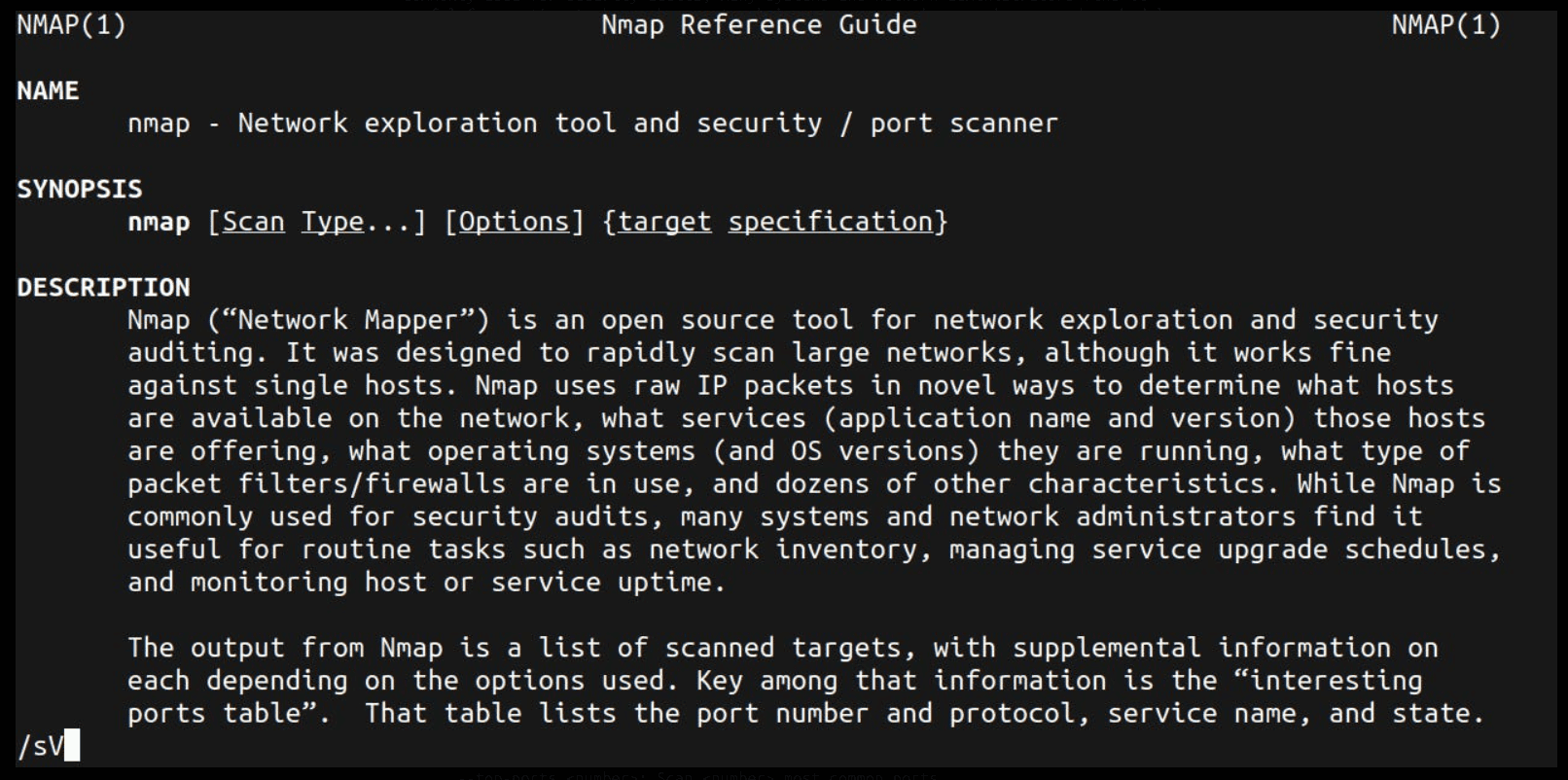
SERVICE/VERSION DETECTION:
-sV: Probe open ports to determine service/version info
Here you can search for anything that you would like to know in the man page. Service/version info is software that is running on the target. For instance, it can be Apache 2.4.65, nginx-1.24 or other types of software. Don’t worry if you don’t understand all of this right now. It will become all clearer as you progress in you Cyber Security journey.
The important thing is to persevere, stay consistent and don’t give up. After all, if you want know something about a specific topic you can always search it in the Internet.
Task 7
What username is able to log into the target over telnet with a blank password?
root
Now, type the following command. Remember to change the IP Address to your own. How did I know that the root was the right answer?
In Cyber Security, you will be called to guess a lot of credentials. Some of the most common ones are the following.
- admin
- administrator
- root
- username
- test
As you progress, there is a list, often in the form of a .txt file, that contains a lot of usernames and passwords and in a sense you test all of them against a target until (hopefully) you find the right combination.
So, we have been lucky for this one.
telnet 10.129.242.37
Trying 10.129.242.37...
Connected to 10.129.242.37.
Escape character is '^]'.
█ █ ▐▌ ▄█▄ █ ▄▄▄▄
█▄▄█ ▀▀█ █▀▀ ▐▌▄▀ █ █▀█ █▀█ █▌▄█ ▄▀▀▄ ▀▄▀
█ █ █▄█ █▄▄ ▐█▀▄ █ █ █ █▄▄ █▌▄█ ▀▄▄▀ █▀█
Meow login: root
Welcome to Ubuntu 20.04.2 LTS (GNU/Linux 5.4.0-77-generic x86_64)
* Documentation: https://help.ubuntu.com
* Management: https://landscape.canonical.com
* Support: https://ubuntu.com/advantage
System information as of Wed 03 Sep 2025 05:54:40 PM UTC
System load: 0.0
Usage of /: 41.7% of 7.75GB
Memory usage: 4%
Swap usage: 0%
Processes: 135
Users logged in: 0
IPv4 address for eth0: 10.129.242.37
IPv6 address for eth0: dead:beef::250:56ff:fe94:a4b2
* Super-optimized for small spaces - read how we shrank the memory
footprint of MicroK8s to make it the smallest full K8s around.
https://ubuntu.com/blog/microk8s-memory-optimisation
75 updates can be applied immediately.
31 of these updates are standard security updates.
To see these additional updates run: apt list --upgradable
The list of available updates is more than a week old.
To check for new updates run: sudo apt update
Ubuntu comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by
applicable law.
Last login: Mon Sep 6 15:15:23 UTC 2021 from 10.10.14.18 on pts/0
root@Meow:~#
Submit Flag
Submit root flag
You are inside the target. If you type the following command you can see the files and folders inside your current location.
ls -l
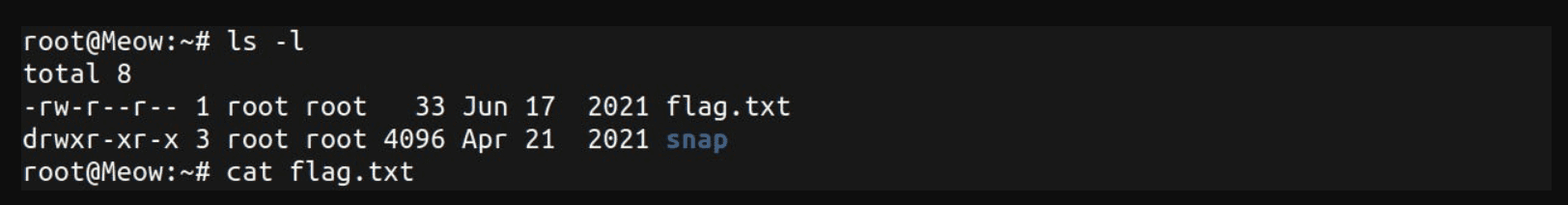
cat flag.txt
The cat command just outputs the contents of the given file. Congratulations! You have solved this machine! 🎉 🎉 🎉
