Hack The Box - Fawn

Howdy my fellow Cyber Enthusiasts! Welcome to the second Starting Point Hack The Box offers. I am excited to embark on this journey with you. So, without further ado, let’s dive in! :)
Need to embark on an exciting journey on Hack The Box? Sign up now using the following Link.
Remember to change the IP adress to your allocated one! :)
There are 2 options available to connect to our machine. First using Pwnbox or secondly using OpenVPN.
I need to mention that if you are using the first option (Pwnbox) you can follow this guide, regardless if you are using Windows, Mac OS or Linux. This is the case, because a new tab will open in your web browser and there you can interact with the target machine.
Now, if you are using Ubuntu-based distros, you can following this guide using the second option as well, but it will not work with a Windows OS for example.
If you want to use the first option, it is very simple. Just click on the option and follow the instructions (Start Pwnbox). A new tab will open up and there you can interact with the machine.
For the second option, things are a bit more complicated. You click on the “Connect using OpenVPN” and the follow section appears. Click on “Download VPN” and save the file on your desired folder.
Then open up the terminal and navigate to the folder that you’ve downloaded the .ovpn file. Then, type the following command (change the filename accordingly).
sudo openvpn root.ovpn
To make sure you are connected to the Hack The Box network type the following command in the terminal.
ip a s
You should see a new connection under the tun0 section. For example, I got a inet 10.10.15.55/23.
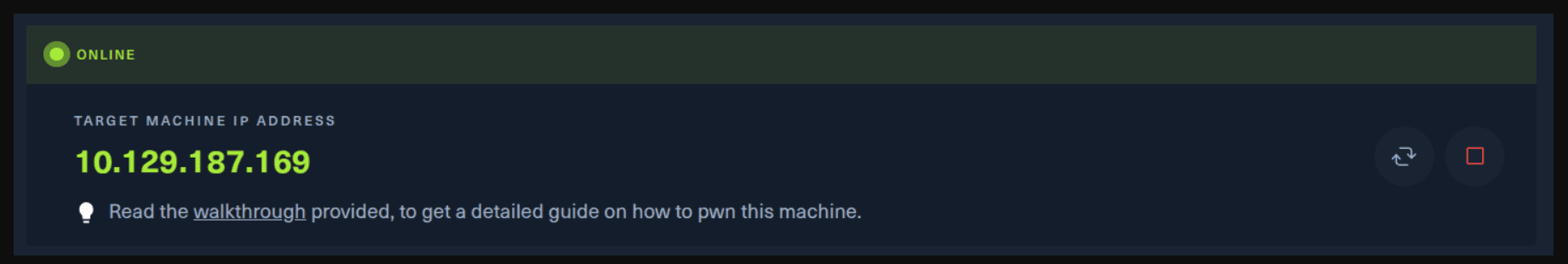
Next, you click on the “Spawn the target machine and the IP will show here“. Wait for a couple of seconds and a target machine IP address will appear. To make sure you can interact with the machine, you can ping it using the terminal to make sure it responds back.
ping -c 3 10.129.187.169
PING 10.129.187.169 (10.129.187.169) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.129.187.169: icmp_seq=1 ttl=63 time=65.3 ms
64 bytes from 10.129.187.169: icmp_seq=2 ttl=63 time=65.2 ms
64 bytes from 10.129.187.169: icmp_seq=3 ttl=63 time=66.2 ms
--- 10.129.187.169 ping statistics ---
3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2002ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 65.162/65.558/66.239/0.483 ms
So, let’s proceed with the questions.
Task 1
What does the 3-letter acronym FTP stand for?
File Transfer Protocol
Open up the terminal and type the following command.
man ftp
The File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a standard communication protocol used for the transfer of computer files from a server to a client on a computer network.
Task 2
Which port does the FTP service listen on usually?
21
Let’s understand this answer by running the following command.
sudo nmap -sV 10.129.187.169
Starting Nmap 7.80 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2025-09-04 16:05 EEST
Nmap scan report for 10.129.187.169
Host is up (0.070s latency).
Not shown: 999 closed ports
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
21/tcp open ftp vsftpd 3.0.3
Service Info: OS: Unix
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 1.77 seconds
We can see that vsftpd 3.0.3 is running at port 21. Although it is common knoweldge in the IT sphere that ftp is usually running at port 21, here how you can find out.
Here is another trick! Go the terminal and type the following command.
man nmap
Probably you see an output of something like this.
Now, type /sV and press Enter. It will update at the left bottom side of the terminal.
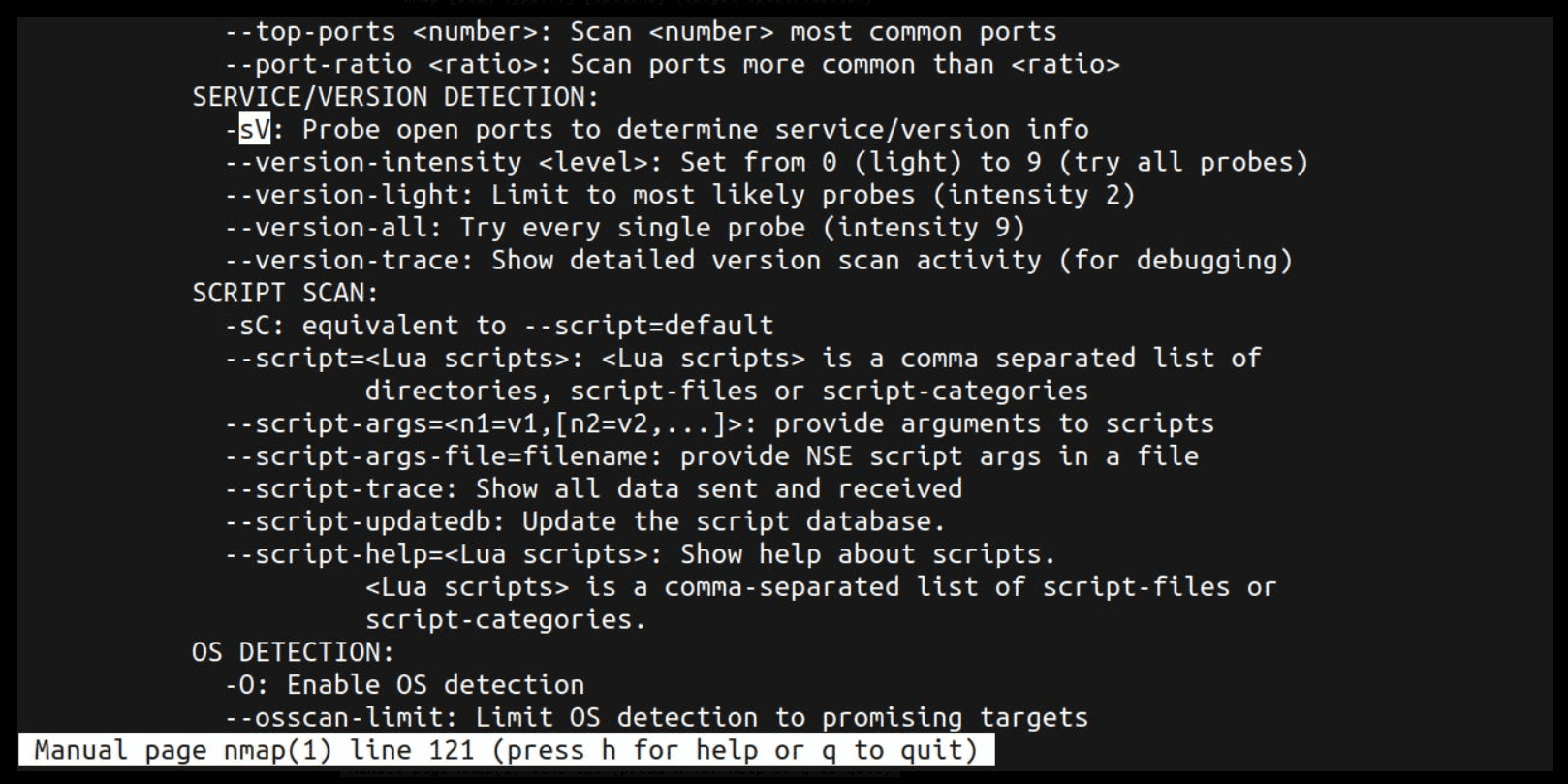
SERVICE/VERSION DETECTION:
-sV: Probe open ports to determine service/version info
Task 3
FTP sends data in the clear, without any encryption. What acronym is used for a later protocol designed to provide similar functionality to FTP but securely, as an extension of the SSH protocol?
SFTP
To learn more about sftp, just use the following command.
man sftp
In computing, the SSH File Transfer Protocol, also known as Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP), is a network protocol that provides file access, file transfer, and file management over any reliable data stream. It was designed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) as an extension of the Secure Shell protocol (SSH) version 2.0 to provide secure file transfer capabilities, and is seen as a replacement of File Transfer Protocol (FTP) due to superior security.
Task 4
What is the command we can use to send an ICMP echo request to test our connection to the target?
ping
Remember?
ping -c 3 10.129.187.169
Task 5
From your scans, what version is FTP running on the target?
vsftpd 3.0.3
Again, remember?
sudo nmap -sV 10.129.187.169
Starting Nmap 7.80 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2025-09-04 16:05 EEST
Nmap scan report for 10.129.187.169
Host is up (0.070s latency).
Not shown: 999 closed ports
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
21/tcp open ftp vsftpd 3.0.3
Service Info: OS: Unix
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 1.77 seconds
Task 6
From your scans, what OS type is running on the target?
Unix
We can see the answer from above.
Service Info: OS: Unix
Task 7
What is the command we need to run in order to display the 'ftp' client help menu?
ftp -?
That one you must know. A quick Internet search will do the job! :)
Task 8
What is username that is used over FTP when you want to log in without having an account?
anonymous
Again, this is a convention used in the cyber security world. This means that some FTP servers accept anonymous connections, meaning that you don’t need to have an account to be able to access some or all of their files.
Task 9
What is the response code we get for the FTP message 'Login successful'?
230
We can run the following command to connect to the FTP server anonymously.
ftp anonymous@10.129.187.169
Connected to 10.129.187.169.
220 (vsFTPd 3.0.3)
331 Please specify the password.
Password:
230 Login successful.
Remote system type is UNIX.
Using binary mode to transfer files.
ftp>
Task 10
There are a couple of commands we can use to list the files and directories available on the FTP server. One is dir. What is the other that is a common way to list files on a Linux system.
ls
You can use the manpage in the terminal to learn more about it. But all it does is simply list files and folders in your current directory.
man ls
Task 11
What is the command used to download the file we found on the FTP server?
get
We can connect to the FTP server using the anonymous credentials. For the password just leave it blank (Press Enter). Inside the FTP server, type help and some useful commands will appear. A lot of programs make use of the help command, so make sure to use it when you are in need. In our case, we need the ‘get’ command to be able to download a file found on the FTP server.
ftp anonymous@10.129.187.169
Connected to 10.129.187.169.
220 (vsFTPd 3.0.3)
331 Please specify the password.
Password:
230 Login successful.
Remote system type is UNIX.
Using binary mode to transfer files.
ftp> help
Commands may be abbreviated. Commands are:
! edit lpage nlist rcvbuf struct
$ epsv lpwd nmap recv sunique
account epsv4 ls ntrans reget system
append epsv6 macdef open remopts tenex
ascii exit mdelete page rename throttle
bell features mdir passive reset trace
binary fget mget pdir restart type
bye form mkdir pls rhelp umask
case ftp mls pmlsd rmdir unset
cd gate mlsd preserve rstatus usage
cdup get mlst progress runique user
chmod glob mode prompt send verbose
close hash modtime proxy sendport xferbuf
cr help more put set ?
debug idle mput pwd site
delete image mreget quit size
dir lcd msend quote sndbuf
disconnect less newer rate status
ftp>
Submit Flag
Submit root flag
Inside the ftp server, just list the contents of the current by simply typing the ls command we’ve learned earlier.
ftp> ls
229 Entering Extended Passive Mode (|||16279|)
150 Here comes the directory listing.
-rw-r--r-- 1 0 0 32 Jun 04 2021 flag.txt
Finally, just use get flag.txt and this command will download the file on your computer.
ftp> get flag.txt
local: flag.txt remote: flag.txt
229 Entering Extended Passive Mode (|||37927|)
150 Opening BINARY mode data connection for flag.txt (32 bytes).
100% |****************************************************| 32 6.69 KiB/s 00:00 ETA
226 Transfer complete.
32 bytes received in 00:00 (0.44 KiB/s)
Finally, open another terminal and use cat flag.txt to see the contents of that file.
cat flag.txt
Congratulations! You have solved this machine! 🎉 🎉 🎉
