Hack The Box - Redeemer

Howdy my fellow Cyber Enthusiasts! Welcome to the first Starting Point Hack The Box offers. I am excited to embark on this journey with you. So, without further ado, let’s dive in! :)
Need to embark on an exciting journey on Hack The Box? Sign up now using the following Link.
Remember to change the IP adress to your allocated one! :)
There are 2 options available to connect to our machine. First using Pwnbox or secondly using OpenVPN.
I need to mention that if you are using the first option (Pwnbox) you can follow this guide, regardless if you are using Windows, Mac OS or Linux. This is the case, because a new tab will open in your web browser and there you can interact with the target machine.
Now, if you are using Ubuntu-based distros, you can following this guide using the second option as well, but it will not work with a Windows OS for example.
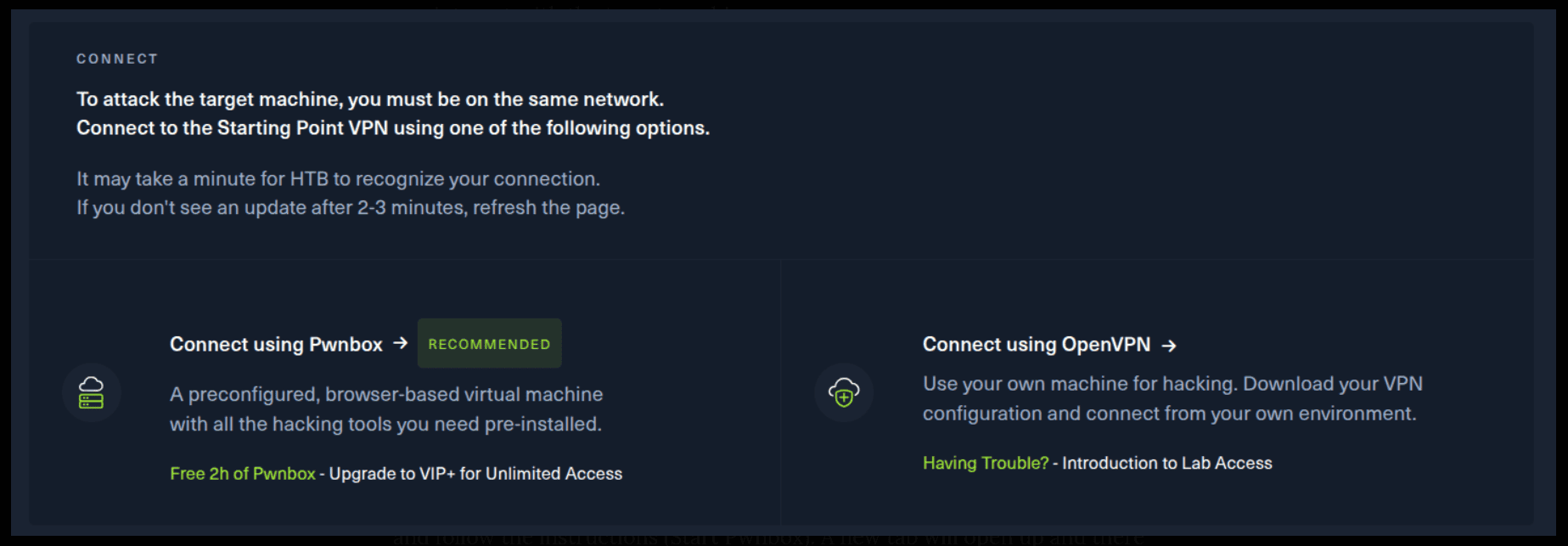
If you want to use the first option, it is very simple. Just click on the option and follow the instructions (Start Pwnbox). A new tab will open up and there you can interact with the machine.
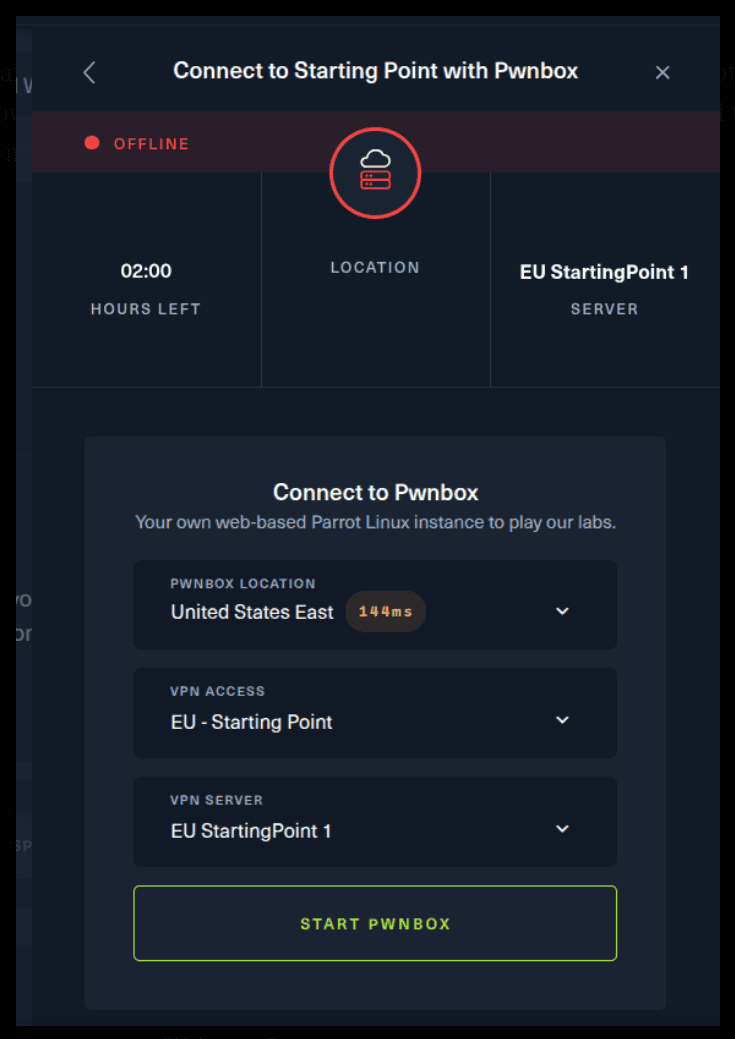
For the second option, things are a bit more complicated. You click on the “Connect using OpenVPN” and the follow section appears. Click on “Download VPN” and save the file on your desired folder.
Then open up the terminal and navigate to the folder that you’ve downloaded the .ovpn file. Then, type the following command (change the filename accordingly).
sudo openvpn root.ovpn
To make sure you are connected to the Hack The Box network type the following command in the terminal.
ip a s
You should see a new connection under the tun0 section. For example, I got a inet 10.10.15.55/23.
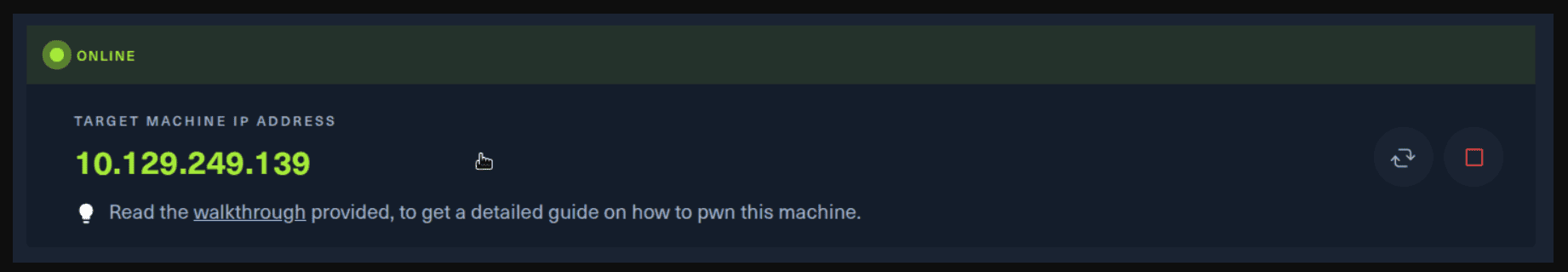
Next, you click on the “Spawn the target machine and the IP will show here“. Wait for a couple of seconds and a target machine IP address will appear. To make sure you can interact with the machine, you can ping it using the terminal to make sure it responds back.
ping -c 3 10.129.249.139
PING 10.129.249.139 (10.129.249.139) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.129.249.139: icmp_seq=1 ttl=63 time=163 ms
64 bytes from 10.129.249.139: icmp_seq=2 ttl=63 time=77.7 ms
64 bytes from 10.129.249.139: icmp_seq=3 ttl=63 time=78.7 ms
--- 10.129.249.139 ping statistics ---
3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2002ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 77.652/106.460/163.031/40.003 ms
Task 1
Which TCP port is open on the machine?
In order to answer this question, we must use a tool called Nmap. Here is a little information about it. I promise, things will become clearer as you progress! :)
In case you are wondering, Nmap (Network Mapper) is a network scanner created by Gordon Lyon. Nmap is used to discover hosts and services on a computer network by sending packets and analyzing the responses. Nmap provides a number of features for probing computer networks, including host discovery and service and operating system detection.
Just run the following command.
-sV: Probe open ports to determine service/version info
-p-: Just runs a scan for all ports ranging from 1-65535
sudo nmap -sV -p- 10.129.249.139
Starting Nmap 7.80 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2025-09-04 21:03 EEST
Nmap scan report for 10.129.249.139
Host is up (0.077s latency).
Not shown: 65534 closed ports
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
6379/tcp open redis Redis key-value store 5.0.7
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 68.88 seconds
We are interested in this piece of information.
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
6379/tcp open redis Redis key-value store 5.0.7
Here is another trick! Go the terminal and type the following command.
man nmap
Probably you see an output of something like this.
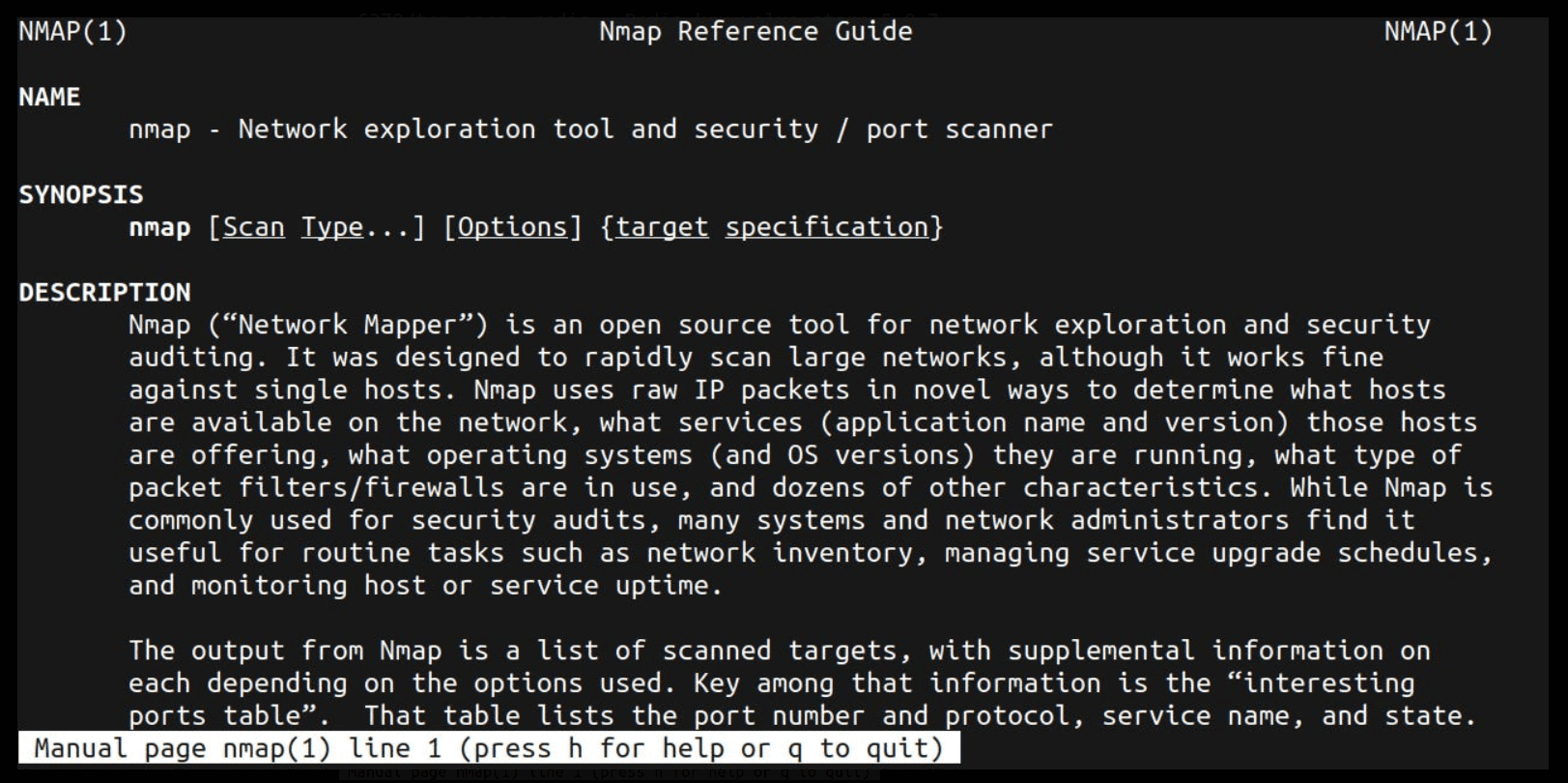
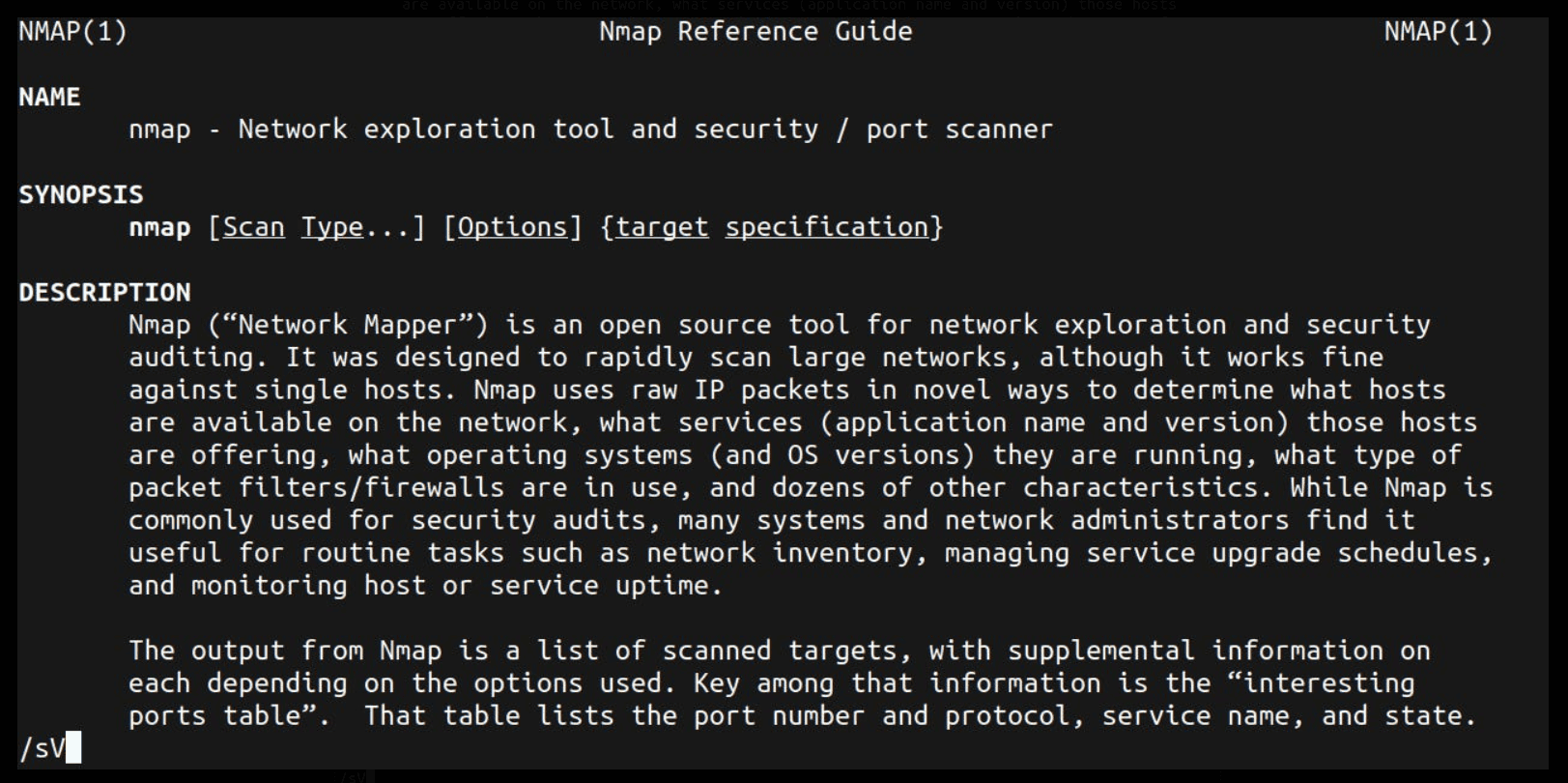
Now, type /sV and press Enter. It will update at the left bottom side of the terminal.
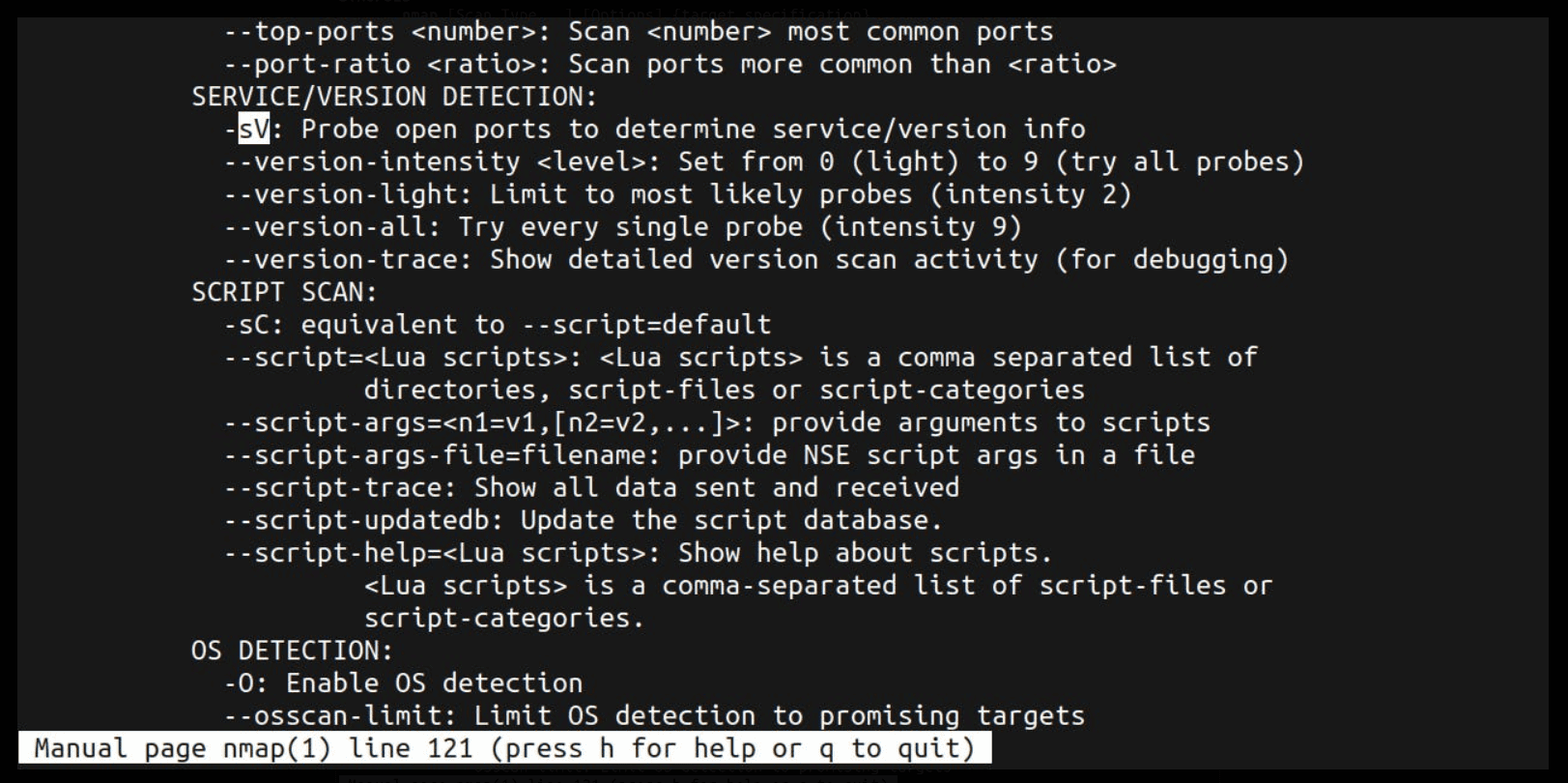
SERVICE/VERSION DETECTION:
-sV: Probe open ports to determine service/version info
Task 2
Which service is running on the port that is open on the machine?
Again, the answer lies in the previous output. Remember?
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
6379/tcp open redis Redis key-value store 5.0.7
Task 3
What type of database is Redis? Choose from the following options: (i) In-memory Database, (ii) Traditional Database
Here is a little information about Redis.
Redis is an in-memory key–value database, used as a distributed cache and message broker, with optional durability. Because it holds all data in memory and because of its design, Redis offers low-latency reads and writes, making it particularly suitable for use cases that require a cache.
Task 4
Which command-line utility is used to interact with the Redis server? Enter the program name you would enter into the terminal without any arguments.
Redis-cli is a command line tool used to interact with the Redis server. Most package managers include redis-cli as part of the redis package. It can also be compiled from source, and you'll find the source code in the Redis repository on GitHub.
You can watch more information on the below link or watch a video here (1:43 of length).
Source: Redis-cli
Task 5
Which flag is used with the Redis command-line utility to specify the hostname?
Try the following command. This is a help page for redis-cli from the terminal.
redis-cli --help
redis-cli 6.0.16
Usage: redis-cli [OPTIONS] [cmd [arg [arg ...]]]
-h <hostname> Server hostname (default: 127.0.0.1).
-p <port> Server port (default: 6379).
-s <socket> Server socket (overrides hostname and port).
-a <password> Password to use when connecting to the server.
You can also use the REDISCLI_AUTH environment
variable to pass this password more safely
(if both are used, this argument takes precedence).
In case you don’t have redis-cli installed on your system you can use the following command to install it for Ubuntu Distributions.
In case you are using PwnBox this command should also work, if the redis-cli is not installed on their system.
sudo apt install redis-cli
We are interested in this portion of the output, because this is what the question asks.
-h <hostname> Server hostname (default: 127.0.0.1).
Task 6
Once connected to a Redis server, which command is used to obtain the information and statistics about the Redis server?
Let’s first connect with the target machine using what we’ve learned earlier.
redis-cli -h 10.129.249.139
10.129.249.139:6379> info
# Server
redis_version:5.0.7
redis_git_sha1:00000000
redis_git_dirty:0
redis_build_id:66bd629f924ac924
redis_mode:standalone
os:Linux 5.4.0-77-generic x86_64
arch_bits:64
multiplexing_api:epoll
atomicvar_api:atomic-builtin
gcc_version:9.3.0
process_id:753
run_id:90929712ec4ede118b4d682b9a3f26ab17539886
tcp_port:6379
uptime_in_seconds:1509
uptime_in_days:0
hz:10
configured_hz:10
lru_clock:12179737
executable:/usr/bin/redis-server
config_file:/etc/redis/redis.conf
Task 7
What is the version of the Redis server being used on the target machine?
We already discovered that above. Look closely.
redis_version:5.0.7
Task 8
Which command is used to select the desired database in Redis?
The following link is very useful for discovering that answer.
Source: Redis Commands
Task 9
How many keys are present inside the database with index 0?
Remember the above command? Look closely at the bottom of that output.
redis-cli -h 10.129.249.139
10.129.249.139:6379> info
# Server
redis_version:5.0.7
redis_git_sha1:00000000
redis_git_dirty:0
redis_build_id:66bd629f924ac924
redis_mode:standalone
// SNIP //
# Keyspace
db0:keys=4,expires=0,avg_ttl=0
10.129.249.139:6379>
Task 10
Which command is used to obtain all the keys in a database?
Have a quick look at the following link.
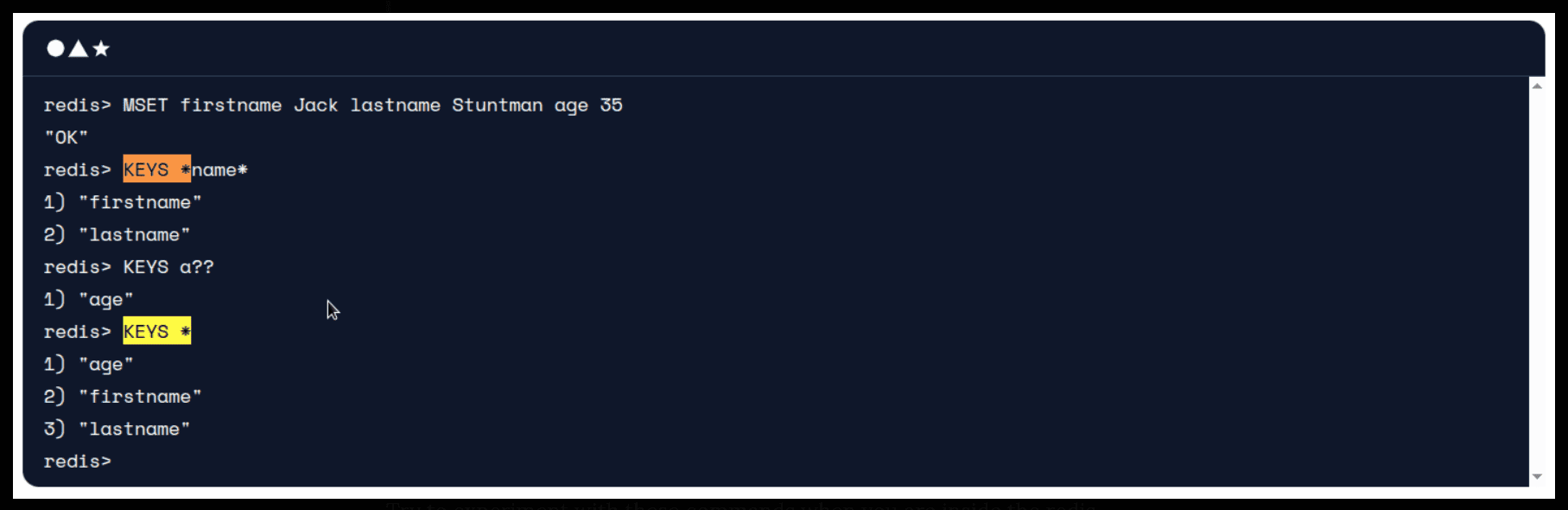
Source: Redis Keys
Try to experiment with these commands when you are inside the redis environment.
10.129.249.139:6379> keys *
1) "numb"
2) "flag"
3) "temp"
4) "stor"
10.129.249.139:6379>
Hmm.. We are seeing a flag. Is this what we are looking for? Let’s see.
10.129.249.139:6379> get numb
"bb2c8a7506ee45cc981eb88bb81dddab"
10.129.249.139:6379> get temp
"1c98492cd337252698d0c5f631dfb7ae"
10.129.249.139:6379> get stor
"e80d635f95686148284526e1980740f8"
10.129.249.139:6379> get flag
It is indeed! Congratulations! You have solved this machine! 🎉 🎉 🎉

