Hack The Box - Crocodile

Howdy my fellow Cyber Enthusiasts! Welcome to the first Starting Point Hack The Box offers. I am excited to embark on this journey with you. So, without further ado, let’s dive in! :)
Need to embark on an exciting journey on Hack The Box? Sign up now using the following Link.
Remember to change the IP adress to your allocated one! :)
There are 2 options available to connect to our machine. First using Pwnbox or secondly using OpenVPN.
I need to mention that if you are using the first option (Pwnbox) you can follow this guide, regardless if you are using Windows, Mac OS or Linux. This is the case, because a new tab will open in your web browser and there you can interact with the target machine.
Now, if you are using Ubuntu-based distros, you can following this guide using the second option as well, but it will not work with a Windows OS for example.
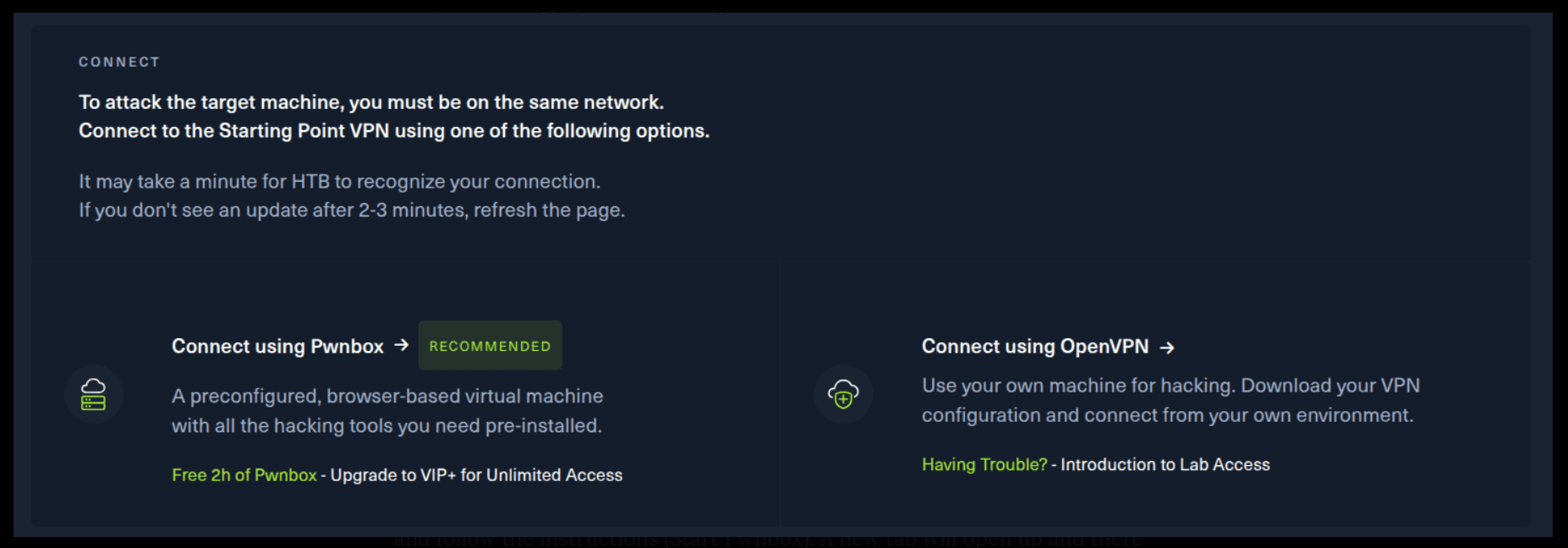
If you want to use the first option, it is very simple. Just click on the option and follow the instructions (Start Pwnbox). A new tab will open up and there you can interact with the machine.
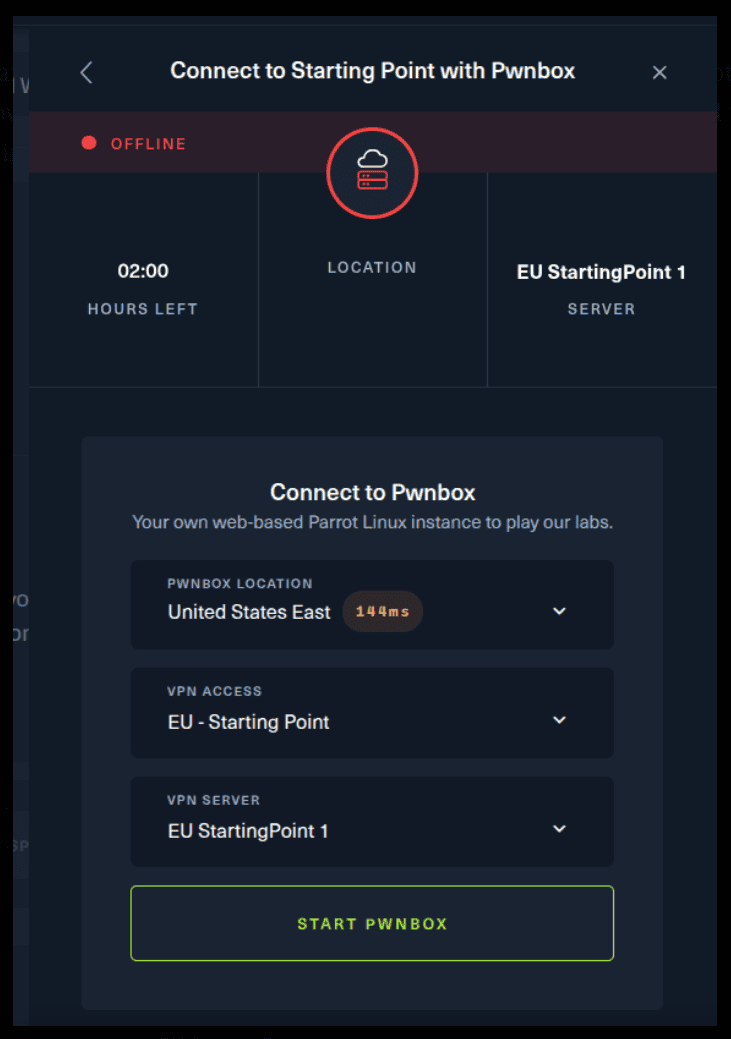
For the second option, things are a bit more complicated. You click on the “Connect using OpenVPN” and the follow section appears. Click on “Download VPN” and save the file on your desired folder.
Then open up the terminal and navigate to the folder that you’ve downloaded the .ovpn file. Then, type the following command (change the filename accordingly).
sudo openvpn root.ovpn
To make sure you are connected to the Hack The Box network type the following command in the terminal.
ip a s
You should see a new connection under the tun0 section. For example, I got a inet 10.10.15.55/23.
Next, you click on the “Spawn the target machine and the IP will show here“. Wait for a couple of seconds and a target machine IP address will appear. To make sure you can interact with the machine, you can ping it using the terminal to make sure it responds back.
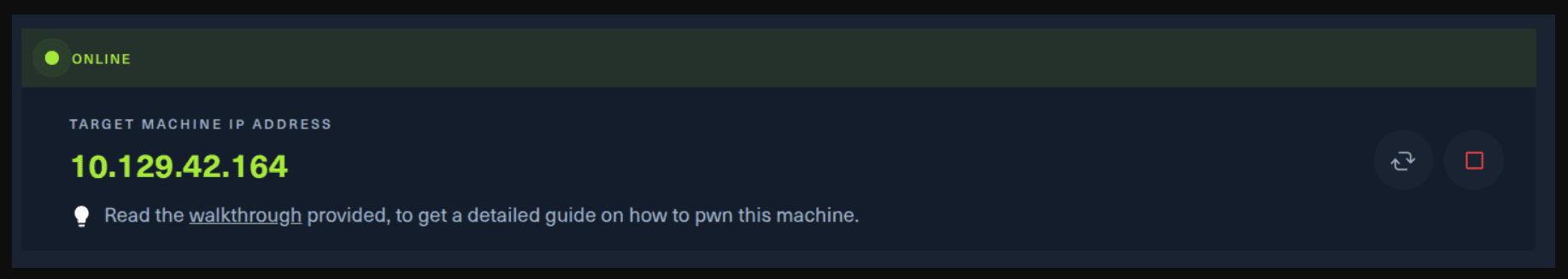
ping -c 3 10.129.42.164
PING 10.129.42.164 (10.129.42.164) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.129.42.164: icmp_seq=1 ttl=63 time=113 ms
64 bytes from 10.129.42.164: icmp_seq=2 ttl=63 time=77.0 ms
64 bytes from 10.129.42.164: icmp_seq=3 ttl=63 time=57.5 ms
--- 10.129.42.164 ping statistics ---
3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2002ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 57.454/82.392/112.695/22.868 ms
Task 1
What Nmap scanning switch employs the use of default scripts during a scan?
In case you are wondering, Nmap (Network Mapper) is a network scanner created by Gordon Lyon. Nmap is used to discover hosts and services on a computer network by sending packets and analyzing the responses. Nmap provides a number of features for probing computer networks, including host discovery and service and operating system detection.
If you want to install nmap in your machine, enter the following command.
sudo apt install nmap
Let’s see a little trick if you want to learn more about a given program. In your terminal type the following.
man nmap
That will provide you with a help page to learn more about nmap. Another trick. When you are inside the man page, do the following.
Type /default, because the question asks as about the use of default scripts, so we are using that as a search keyword.
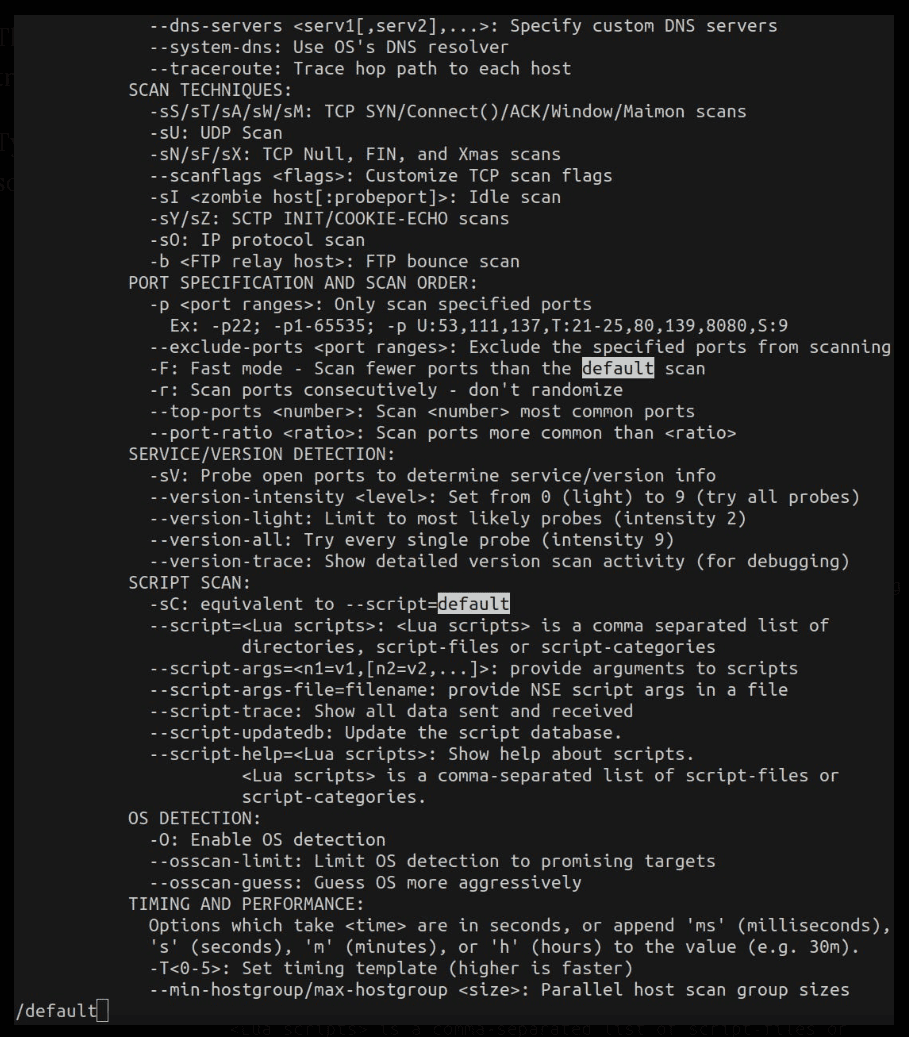
SCRIPT SCAN:
-sC: equivalent to --script=default
Task 2
What service version is found to be running on port 21?
Let’s run a nmap scan against our target machine.
-sV specifies service version
-p 21 specifies to scan only port 21
sudo nmap -sV -p 21 10.129.42.164
Starting Nmap 7.80 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2025-09-09 18:14 EEST
Nmap scan report for 10.129.42.164
Host is up (0.11s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
21/tcp open ftp vsftpd 3.0.3
Service Info: OS: Unix
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.74 seconds
Task 3
What FTP code is returned to us for the "Anonymous FTP login allowed" message?
If we want to connect to the FTP of our target machine we can use the following command. Keep in mind that there is no password needed when we are connected as an anonymous user.
ftp anonymous@10.129.42.164
Connected to 10.129.42.164.
220 (vsFTPd 3.0.3)
230 Login successful.
Remote system type is UNIX.
Using binary mode to transfer files.
ftp>
Task 4
After connecting to the FTP server using the ftp client, what username do we provide when prompted to log in anonymously?
anonymous is the user that we are connecting as to the FTP server of our target machine.
ftp anonymous@10.129.42.164
Task 5
After connecting to the FTP server anonymously, what command can we use to download the files we find on the FTP server?
First, let’s list the folders/files on our current directory. We can do that with the following command.
ftp> dir
229 Entering Extended Passive Mode (|||43472|)
150 Here comes the directory listing.
-rw-r--r-- 1 ftp ftp 33 Jun 08 2021 allowed.userlist
-rw-r--r-- 1 ftp ftp 62 Apr 20 2021 allowed.userlist.passwd
226 Directory send OK.
Then, use the get command to download the specified files.
ftp> get allowed.userlist
local: allowed.userlist remote: allowed.userlist
229 Entering Extended Passive Mode (|||49529|)
150 Opening BINARY mode data connection for allowed.userlist (33 bytes).
100% |****************************************************| 33 0.50 KiB/s 00:00 ETA
226 Transfer complete.
33 bytes received in 00:00 (0.09 KiB/s)
ftp> get allowed.userlist.passwd
local: allowed.userlist.passwd remote: allowed.userlist.passwd
229 Entering Extended Passive Mode (|||46672|)
150 Opening BINARY mode data connection for allowed.userlist.passwd (62 bytes).
100% |****************************************************| 62 0.93 KiB/s 00:00 ETA
226 Transfer complete.
62 bytes received in 00:00 (0.17 KiB/s)
ftp>
Task 6
What is one of the higher-privilege sounding usernames in 'allowed.userlist' that we download from the FTP server?
Next, open up another terminal and navigate to the directory that the above files were downloaded. We can see their contents by using the following command.
cat allowed.userlist
cat allowed.userlist.passwd
Try out the usernames in the allowed.userlist file.
Task 7
What version of Apache HTTP Server is running on the target host?
sudo nmap -sV -sC -p 80 10.129.42.164
The Apache HTTP Server is running on port 80 on the target host, so we specify it using -p 80.
Starting Nmap 7.80 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2025-09-09 20:22 EEST
Nmap scan report for 10.129.42.164
Host is up (0.082s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.4.41 ((Ubuntu))
|_http-server-header: Apache/2.4.41 (Ubuntu)
|_http-title: Smash - Bootstrap Business Template
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 11.42 seconds
Task 8
What switch can we use with Gobuster to specify we are looking for specific filetypes?
You can always use the help page provided by gobuster. Look out for the answer in the output.
gobuster --help
Usage of gobuster:
-P string
Password for Basic Auth (dir mode only)
-U string
Username for Basic Auth (dir mode only)
-a string
Set the User-Agent string (dir mode only)
-c string
Cookies to use for the requests (dir mode only)
-cn
Show CNAME records (dns mode only, cannot be used with '-i' option)
-e Expanded mode, print full URLs
-f Append a forward-slash to each directory request (dir mode only)
-fw
Force continued operation when wildcard found
-i Show IP addresses (dns mode only)
-k Skip SSL certificate verification
-l Include the length of the body in the output (dir mode only)
-m string
Directory/File mode (dir) or DNS mode (dns) (default "dir")
-n Don't print status codes
-np
Don't display progress
-o string
Output file to write results to (defaults to stdout)
-p string
Proxy to use for requests [http(s)://host:port] (dir mode only)
-q Don't print the banner and other noise
-r Follow redirects
-s string
Positive status codes (dir mode only) (default "200,204,301,302,307,403")
-t int
Number of concurrent threads (default 10)
-to duration
HTTP Timeout in seconds (dir mode only) (default 10s)
-u string
The target URL or Domain
-v Verbose output (errors)
-w string
Path to the wordlist
-x string
File extension(s) to search for (dir mode only)
Task 9
Which PHP file can we identify with directory brute force that will provide the opportunity to authenticate to the web service?
We need to use gobuster to find that answer. Probably, if you are using Pwnbox this is already installed. You can install gobuster by visiting the following Github link.
Source: Gobuster
At the time of writing the github owner recommends installing gobuster using the following command.
go install github.com/OJ/gobuster/v3@latest
Of course, we need to be able to install Go to do that. You can follow the instructions in the below link to do that.
Source: Install Go
We can see our Go version using the following command.
go version
go version go1.25.1 linux/amd64
Next, download this .txt file to find out folders and .php files in our target machine.
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/v0re/dirb/master/wordlists/common.txt
Then, let’s see gobuster in action.
gobuster dir -u http://10.129.42.164 -w common.txt -x .php
===============================================================
Gobuster v3.8.2
by OJ Reeves (@TheColonial) & Christian Mehlmauer (@firefart)
===============================================================
[+] Url: http://10.129.42.164
[+] Method: GET
[+] Threads: 10
[+] Wordlist: common.txt
[+] Negative Status codes: 404
[+] User Agent: gobuster/3.8.2
[+] Extensions: php
[+] Timeout: 10s
===============================================================
Starting gobuster in directory enumeration mode
===============================================================
assets (Status: 301) [Size: 315] [--> http://10.129.42.164/assets/]
config.php (Status: 200) [Size: 0]
css (Status: 301) [Size: 312] [--> http://10.129.42.164/css/]
dashboard (Status: 301) [Size: 318] [--> http://10.129.42.164/dashboard/]
fonts (Status: 301) [Size: 314] [--> http://10.129.42.164/fonts/]
index.html (Status: 200) [Size: 58565]
js (Status: 301) [Size: 311] [--> http://10.129.42.164/js/]
login.php (Status: 200) [Size: 1577]
logout.php (Status: 302) [Size: 0] [--> login.php]
server-status (Status: 403) [Size: 278]
Progress: 9274 / 9274 (100.00%)
===============================================================
Finished
===============================================================
Submit Flag
Submit root flag
Finally, let’s open up our browser on [TARGET_IP/login.php]. Remember these files?
cat allowed.userlist
cat allowed.userlist.passwd
Use admin as the username and the password is all yours! :) Congratulations! You have solved this machine! 🎉 🎉 🎉
